Published online Dec 16, 2023. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v15.i12.690
Peer-review started: September 21, 2023
First decision: October 24, 2023
Revised: October 25, 2023
Accepted: November 24, 2023
Article in press: November 24, 2023
Published online: December 16, 2023
Processing time: 84 Days and 12.8 Hours
Accurate diagnosis and early resection of colorectal polyps are important to prevent the occurrence of colorectal cancer. However, technical factors and morphological factors of polyps itself can lead to missed diagnoses. Image-enhanced endoscopy and chromoendoscopy (CE) have been developed to faci
To investigate the visibility of margins and surfaces with the combination of TXI and CE for colorectal lesions.
This retrospective study included patients who underwent lower gastrointestinal endoscopy at the Toyoshima Endoscopy Clinic. We extracted polyps that were resected and diagnosed as adenomas or serrated polyps (hyperplastic polyps and sessile serrated lesions) from our endoscopic database. An expert endoscopist performed the lower gastrointestinal endoscopies and observed the lesion using white light imaging (WLI), TXI, CE, and TXI + CE modalities. Indigo carmine dye was used for CE. Three expert endoscopists rated the visibility of the margin and surface patterns in four ranks, from 1 to 4. The primary outcomes were the aver
A total of 48 patients with 81 polyps were assessed. The histological subtypes included 50 tubular adenomas, 16 hyperplastic polyps, and 15 sessile serrated lesions. The visibility scores for the margins based on WLI, TXI, CE, and TXI + CE were 2.44 ± 0.93, 2.90 ± 0.93, 3.37 ± 0.74, and 3.75 ± 0.49, respectively. The visibility scores for the surface based on WLI, TXI, CE, and TXI + CE were 2.25 ± 0.80, 2.84 ± 0.84, 3.12 ± 0.72, and 3.51 ± 0.60, respectively. The visibility scores for the detection and surface on TXI were significantly lower than that on CE but higher than that on WLI (P < 0.001). The visibility scores for the margin and surface on TXI + CE were significantly higher than those on CE (P < 0.001). In the sub-analysis of adenomas, the visibility for the margin and surface on TXI + CE was significantly better than that on WLI, TXI, and CE (P < 0.001). In the sub-analysis of serrated polyps, the visibility for the margin and surface on TXI + CE was also significantly better than that on WLI, TXI, and CE (P < 0.001).
TXI + CE enhanced the visibility of the margin and surface compared to WLI, TXI, and CE for colorectal lesions.
Core Tip: The visibility of colorectal tumors was investigated using texture and color enhancement imaging (TXI) and chromoendoscopy (CE). The combination of TXI and CE showed higher visibility than white-light imaging, TXI, or CE alone for the margins and surfaces of colorectal adenomas and serrated polyps.
- Citation: Hiramatsu T, Nishizawa T, Kataoka Y, Yoshida S, Matsuno T, Mizutani H, Nakagawa H, Ebinuma H, Fujishiro M, Toyoshima O. Improved visibility of colorectal tumor by texture and color enhancement imaging with indigo carmine. World J Gastrointest Endosc 2023; 15(12): 690-698
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5190/full/v15/i12/690.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4253/wjge.v15.i12.690
Colorectal cancer is the third most common malignancy. Accurate diagnosis and early resection of colorectal adenomas are important for preventing the development of colorectal cancer[1,2]. Endoscopic resection of colorectal polyps contributes to over 50% reduction in colorectal cancer mortality, which is the basis for the importance of endoscopic resection[3]. However, 28% of polyps are missed on white light imaging (WLI)[4]. The causes of missed polyps include technical factors and morphological factors of polyps itself, such as superficial types, which are often overlooked[5].
Chromoendoscopy (CE) and image-enhanced endoscopy (IEE) have been developed[6]. Dye-based CE enhances the appearance of the mucosal surface and color patterns, which improves lesion recognition. Indigo carmine highlights the demarcation line of neoplastic lesions, and improves the detection. Pancolonic CE significantly increased the detection rates of adenomas and serrated lesions[7].
IEE includes narrowband imaging, linked color imaging (LCI), and texture and color enhancement imaging (TXI). The TXI mode is characterized by the adjustment of texture and brightness and the enhancement of color[8] and was installed in a new EVIS X1 endoscopy system (Olympus Corporation, Tokyo, Japan). Regarding the TXI principle, the image captured from WLI was separated into a base and a detailed image. The texture and brightness of the two images were adjusted. These were then recombined and called TXI mode 2. Furthermore, color enhancement was applied, and it was called TXI mode 1. We previously reported that TXI showed better visibility than WLI for colorectal adenoma[9] and serrated polyps, including sessile serrated lesions[10].
Recently, Okimoto et al[11] reported that magnified endoscopy with TXI and CE improved the visibility of duodenal tumor. There has also been a case report showing the usefulness of TXI and CE in early gastric cancer[12]. However, there have been no reports on the visibility of colorectal tumors using a combination of TXI and CE. Therefore, we examined the efficacy of TXI + CE in colorectal adenomas and serrated polyps. TXI + CE was compared with CE, TXI, and WLI for visibility of the margin and surface pattern.
This retrospective study included patients who underwent lower gastrointestinal endoscopy at the Toyoshima Endoscopy Clinic between May and June 2022. We removed polyps suspected to be cancerous, adenomatous, or clinically significant serrated polyps[2,13]. All resected lesions were pathologically diagnosed using hematoxylin and eosin staining. Patients diagnosed with adenomas or serrated polyps (sessile serrated lesions or hyperplastic polyps) were enrolled in this study. Polyps diagnosed as normal or other, were excluded. We excluded patients with poor bowel preparation or ulcerative colitis. Indications for lower gastrointestinal were investigation of symptoms, such as hematochezia or abdominal pain, investigation of a positive fecal occult blood test, and screening.
This study complied with the Ethical Guidelines for Medical Studies in Japan and the Declaration of Helsinki. The study was approved by the certified ethics committee of the Yoyogi Mental Clinic (certificate number: RKK227). We published this study’s protocol on the website of the Toyoshima Endoscopy Clinic, allowing patients to opt out of the study if desired.
The Toyoshima Endoscopy Clinic has introduced the EVIS X1 video system center, a 4 K resolution ultra-high-definition display monitor, and utilized colonoscopes PCF-H290ZI and CF-HQ290ZI (Olympus, Japan). We used the TXI Mode 1. The TXI Mode 2 is same as TXI mode 1 without color enhancement[14]. CE was performed by spraying 0.05% indigo carmine[15]. The endoscopic pictures and the endoscopic reports were stored with the T-File System (STS-Medic Inc., Tokyo, Japan)[16].
A board certified fellow/trainer of the Japan Gastroenterological Endoscopy Society (Toyoshima O) performed the lower gastrointestinal endoscopy and observed the lesions with the WLI, TXI, CE, and TXI + CE. Firstly, the lesions were cleaned with water. Images of the WLI and TXI were captured. Then, indigo carmine was sprinkled, and CE and TXI + CE images were captured.
The visibility of the margins and surface patterns was surveyed. The definition of margin was the detectability of the lesion border without magnification[9]. The definition of surface patterns was the mucosal structures, including granular, villous, lobular, pit, and superficial microvessel patterns. According to the previous treatises, the visibility score was as follows: A score of 1 was not detectable without repeated careful observation. A score of 2 was considered fair (barely detectable without careful observation). A score of 3 was considered acceptable (detectable without careful observation). A score of 4 was considered excellent (easily detectable)[10,17]. Three expert endoscopists rated the visibility the visibility in four ranks. An expert endoscopist was defined as one who has conducted > 5000 colonoscopies[9,18]. This study did not include magnified observations.
The primary outcomes were the average visibility scores for the margin and surface patterns based on WLI, TXI, CE, and TXI + CE. We compiled information on histological subtype, polyp location, size, and morphology based on the Paris endoscopic classification[19].
Visibility scores between the four modalities were compared by the Kruskal-Wallis and Dunn tests[10]. Stat Mate IV software (version 4.01, ATOMS, Japan) was used for the statistical analysis. The definition of statistical significance was P value < 0.05.
Table 1 shows the clinicopathological characteristics of the 81 polyps enrolled in our study. Histologically, 50 (61.7%) of the 81 polyps were tubular adenomas, 15 (18.5%) were sessile serrated lesions, and 16 (19.8%) were hyperplastic. Regarding tumor location, 7 polyps (8.6%) were in the cecum, 18 (22.2%) in the ascending colon, 39 (48.1%) in the transverse colon, 6 (7.4%) in the descending colon, 9 (11.1%) in the sigmoid colon, and 2 (2.5%) in the rectum. The average tumor size was 5.8 ± 3.7 mm. Macroscopic findings were as follows: 1 (1.2%) 0-Is, 76 (93.8%) 0-IIa, and 4 (4.9%) 0-IIb in the Paris endoscopic classification. Figure 1 shows a design flowchart for this study.
| Polyps, n | 81 |
| Histological subtype, n | |
| Tubular adenoma | 50 |
| Sessile serrated lesion | 15 |
| Hyperplastic polyp | 16 |
| Location; n, cecum, ascending, transverse, descending, sigmoid, rectum | 7, 18, 39, 6, 9, 2 |
| Size, average (standard deviation, range); mm | 5.8 (3.67, 1-20) |
| Morphology; n, 0-Is, 0-IIa, 0-IIb | 1, 76, 4 |
The visibility scores for the margin and surface on TXI were significantly lower than that on CE but higher than that on WLI. The visibility scores for the margins and surface on TXI + CE were significantly higher than those on CE (P < 0.001) (Table 2).
| WLI | TXI | CE | TXI + CE | WLI vs TXI, P value | TXI vs CE, P value | CE vs TXI + CE, P value | |
| Margin, mean (SD) | 2.44 (0.93) | 2.90 (0.93) | 3.37 (0.74) | 3.75 (0.49) | < 0.001 | < 0.001 | < 0.001 |
| Surface, mean (SD) | 2.25 (0.80) | 2.84 (0.84) | 3.12 (0.72) | 3.51 (0.60) | < 0.001 | < 0.01 | < 0.001 |
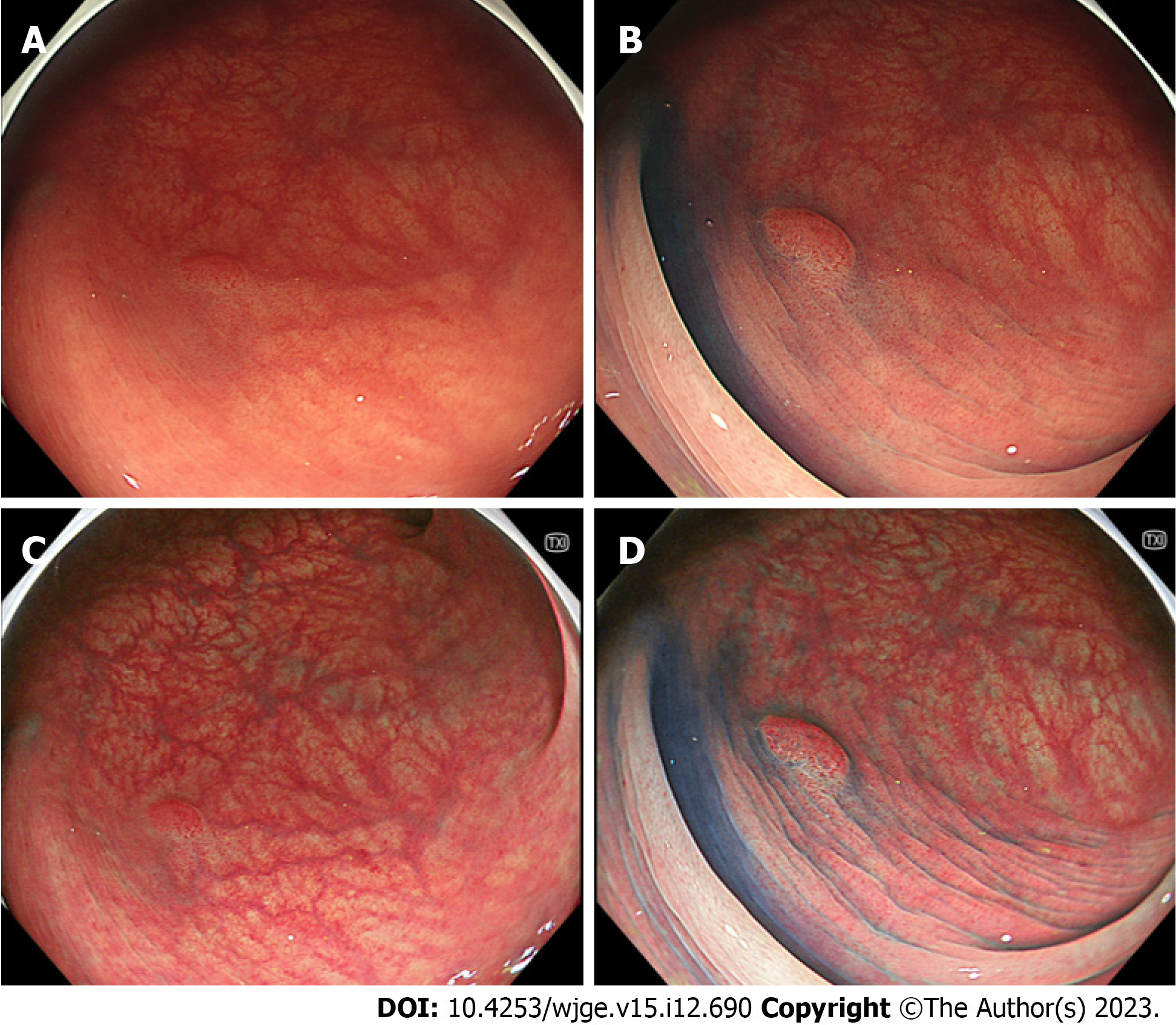
In the sub-analysis of adenomas, the visibility score for the margin of TXI was significantly lower than that of CE but higher than that of WLI. The visibility for the margin on TXI + CE was significantly better than that on CE (P < 0.001) (Table 3). In the sub-analysis of adenomas, the visibility for the surface on TXI was significantly better than that of WLI. No statistically significant differences were observed between the TXI and CE. The visibility for the surface on TXI + CE was significantly better than that on CE (Table 3). Figure 2 shows representative images of adenoma.
| WLI | TXI | CE | TXI + CE | WLI vs TXI, P value | TXI vs CE, P value | CE vs TXI + CE, P value | |
| Margin, mean (SD) | 2.54 (0.84) | 3.00 (0.85) | 3.46 (0.72) | 3.81 (0.42) | < 0.001 | < 0.001 | < 0.001 |
| Surface, mean (SD) | 2.34 (0.75) | 2.93 (0.79) | 3.19 (0.70) | 3.58 (0.56) | < 0.001 | NS | < 0.001 |
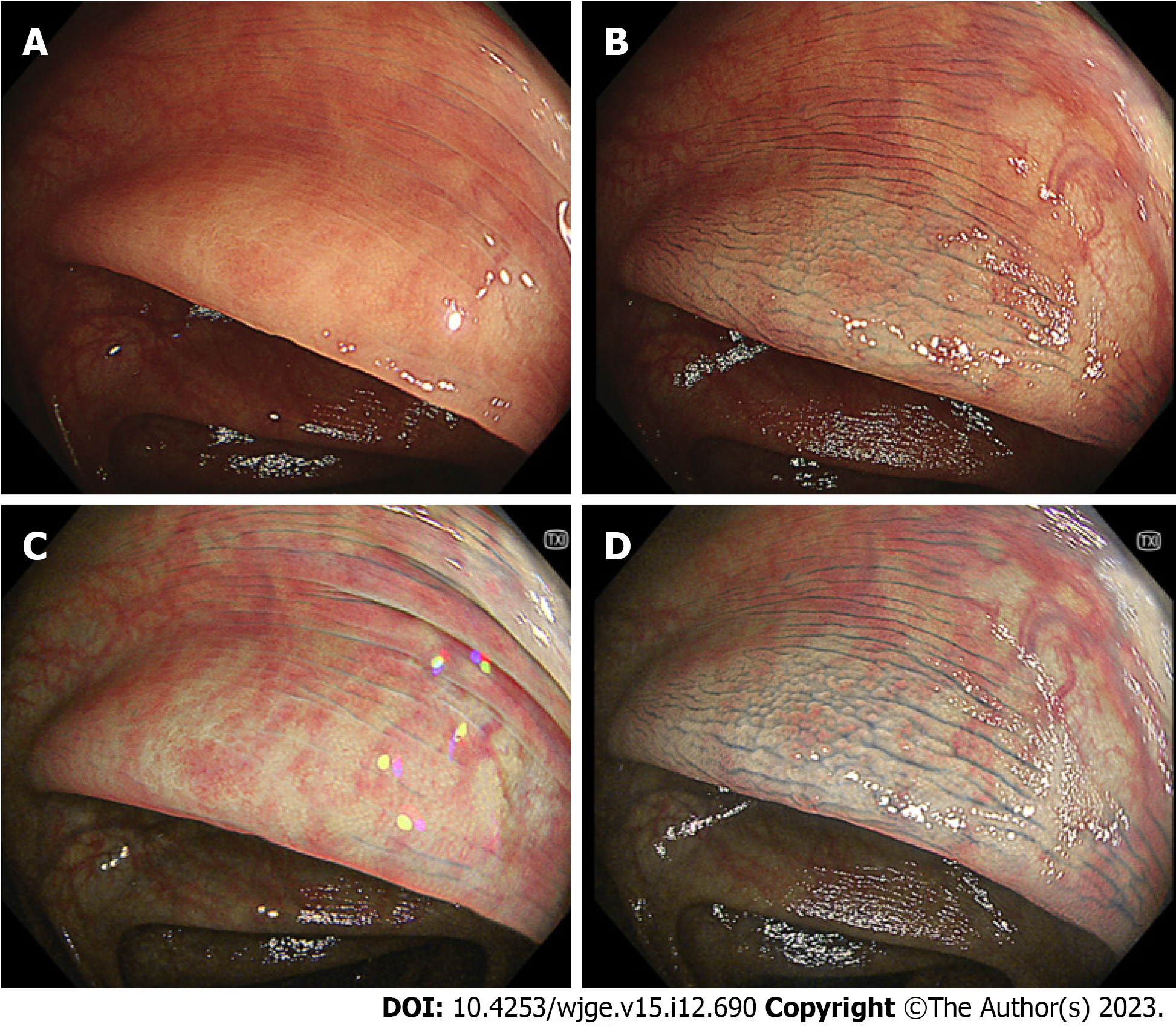
In the sub-analysis of serrated polyps, the visibility score for the margin on TXI was significantly lower than that on CE but higher than that on WLI. The visibility for the margin on TXI + CE was significantly better than that on CE (P < 0.01) (Table 4). In the sub-analysis of serrated polyps, the visibility for the surface on TXI was significantly better than that on WLI. No statistically significant differences were observed between the TXI and CE. The visibility for the surface on TXI + CE was significantly better than that on CE (Table 4). Figure 3 shows representative images of serrated polyp (sessile serrated lesion).
| WLI | TXI | CE | TXI + CE | WLI vs TXI, P value | TXI vs CE, P value | CE vs TXI + CE, P value | |
| Margine, mean (SD) | 2.29 (1.05) | 2.73 (1.03) | 3.23 (0.75) | 3.63 (0.56) | < 0.05 | < 0.05 | < 0.01 |
| Surface, mean (SD) | 2.11 (0.86) | 2.69 (0.89) | 3.01 (0.75) | 3.41 (0.66) | < 0.001 | NS | < 0.01 |
The present study showed that the visibility of the margins and surfaces of colorectal lesions was in the order of TXI + CE, CE, TXI, and WLI, with TXI + CE being the best. In the sub-analysis of adenomas and serrated polyps, TXI + CE provided better visibility than WLI, TXI, or CE. This is the first report on the superiority of TXI + CE in colorectum.
Fujifilm corporation developed an LCI, which is considered a virtual CE. Yoshida et al[20] demonstrated that LCI improved the visibility scores of polyps compared with WLI. Suzuki et al[21] conducted an international randomized control trial that showed that LCI increased the adenoma detection rate compared to WLI (58.7% vs 45.7%; P < 0.01). LCI-based observations are becoming routine in clinical practice and could decrease interval cancer rate[22].
Recently, Olympus developed the TXI as a mode corresponding to LCI. Although TXI is similar to LCI in terms of this concept, the TXI algorithm differs from that of LCI. LCI uses narrowband light, the images are converted to those similar to WLI, and the color is enhanced from red to vivid red, and white to clear white. On the other hand, TXI uses white light without narrowband light, enriches texture and color, and selectively enhances brightness in dark areas[14,23]. TXI enhances slight changes in the structure and color of images that are difficult to observe using WLI.
We previously reported that TXI had better visibility than WLI for colorectal adenomas, regardless of the endoscopist’s experiences[9]. Furthermore, TXI showed better visibility than WLI for colorectal serrated polyps[10]. In this study, the visibility on TXI was better than that on WLI for adenomas and serrated polyps, consistent with previous reports.
Both TXI and CE improve the visibility of colorectal lesions. CE has been reported to increase adenoma detection rate significantly[24,25]. Pohl et al[7] showed that pancolonic CE significantly improved the detection rate for adenomas (0.95 vs 0.66 per patient) and serrated lesions (1.19 vs 0.49 per patient) (P < 0.001). Our study also showed that the visibility on CE was better than that on WLI for adenomas and serrated polyps, consistent with previous reports.
For CE it takes time to sprinkle indigo carmine and suck out the excess. Pohl et al[7] reported that the extubation time in the pancolonic CE group was significantly longer than that in the control group (11.6 min vs 10.1 min; P < 0.001), but the difference was relatively small. They concluded that pancolonic CE was acceptable for routine clinical practice. The cost of indigo carmine is also an issue in pancolonic CE [1.75 $ (245 yen) for one ampule (20 mg/5 mL) of indigo carmine; Daiichi Sankyo Company, Limited, Japan]. Indigo carmine in ampule can also be used for intravenous injection; using it for endoscopic spray is expensive. We used the guaranteed reagent of indigo carmine [50.7 $ (7100 yen), 25 g powder; Fujifilm Wako Pure Chemical Corporation, Japan] in our study and diluted the solution to 0.05%[26]. This method required some time but reduced the cost of indigo carmine by 2.3%.
Magnified endoscopy with TXI and CE has been reported to provide higher visibility of duodenal tumors. Our study confirmed that the combination of TXI and CE was effective in visualizing colorectal lesions. Furthermore, our study used non-magnified endoscopy. TXI + CE is also suitable for observing the colon from a distant view. Although indigo carmine spray decreased the brightness of the entire endoscopic field, TXI adjusted the brightness. Taken together, these results suggest that TXI + CE can replace WLI in routine colonoscopy.
There are several limitations in our study. Although significant differences were statistically confirmed, this was a pilot study conducted at a single center with a sample size of 81 participants. This study was retrospective and included a potential selection bias. Therefore, prospective randomized control trials are desired to verify these findings.
TXI + CE enhanced the visibility of the margins and surface of colorectal lesions compared to WLI, TXI, and CE.
Texture and color enhancement imaging (TXI) was developed to provide higher visibility of colorectal lesions. Chro
There is no literature regarding visibility on the combination of TXI and CE for colorectal tumors.
This study assessed the effectiveness of TXI + CE for the treatment of colorectal adenomas and serrated polyps.
Endoscopic images of adenomas or serrated polyps were obtained with white light imaging (WLI), TXI, CE, and TXI + CE modalities. Expert endoscopists evaluated the visibility scores of the margins and surface patterns. The visibility scores were given in four ranks.
The visibility of margins and surfaces of the colorectal lesions was in the order of TXI + CE, CE, TXI, and WLI, with TXI + CE being the best. In the sub-analysis of adenomas and serrated polyps, the visibility for the margins and surface on TXI + CE was significantly better than that on WLI, TXI, and CE alone (P < 0.001).
Regarding the visibility of margins and surface of colorectal lesions, the combination of TXI + CE was better than that of WLI, TXI, and CE alone.
A prospective randomised controlled trial is desired to confirm these findings.
| 1. | Toyoshima O, Nishizawa T, Yoshida S, Watanabe H, Odawara N, Sakitani K, Arano T, Takiyama H, Kobayashi H, Kogure H, Fujishiro M. Brown slits for colorectal adenoma crypts on conventional magnifying endoscopy with narrow band imaging using the X1 system. World J Gastroenterol. 2022;28:2748-2757. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in CrossRef: 9] [Cited by in RCA: 10] [Article Influence: 2.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 2. | Toyoshima O, Nishizawa T, Yoshida S, Sekiba K, Kataoka Y, Hata K, Watanabe H, Tsuji Y, Koike K. Expert endoscopists with high adenoma detection rates frequently detect diminutive adenomas in proximal colon. Endosc Int Open. 2020;8:E775-E782. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 16] [Cited by in RCA: 18] [Article Influence: 3.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 3. | Zauber AG, Winawer SJ, O'Brien MJ, Lansdorp-Vogelaar I, van Ballegooijen M, Hankey BF, Shi W, Bond JH, Schapiro M, Panish JF, Stewart ET, Waye JD. Colonoscopic polypectomy and long-term prevention of colorectal-cancer deaths. N Engl J Med. 2012;366:687-696. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 1952] [Cited by in RCA: 2392] [Article Influence: 170.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (2)] |
| 4. | Heresbach D, Barrioz T, Lapalus MG, Coumaros D, Bauret P, Potier P, Sautereau D, Boustière C, Grimaud JC, Barthélémy C, Sée J, Serraj I, D'Halluin PN, Branger B, Ponchon T. Miss rate for colorectal neoplastic polyps: a prospective multicenter study of back-to-back video colonoscopies. Endoscopy. 2008;40:284-290. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 351] [Cited by in RCA: 381] [Article Influence: 21.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 5. | Sakamoto T, Ikematsu H, Tamai N, Mizuguchi Y, Takamaru H, Murano T, Shinmura K, Sasabe M, Furuhashi H, Sumiyama K, Saito Y. Detection of colorectal adenomas with texture and color enhancement imaging: Multicenter observational study. Dig Endosc. 2023;35:529-537. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in RCA: 26] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 6. | Shahsavari D, Waqar M, Thoguluva Chandrasekar V. Image enhanced colonoscopy: updates and prospects-a review. Transl Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2023;8:26. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in RCA: 17] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 7. | Pohl J, Schneider A, Vogell H, Mayer G, Kaiser G, Ell C. Pancolonic chromoendoscopy with indigo carmine versus standard colonoscopy for detection of neoplastic lesions: a randomised two-centre trial. Gut. 2011;60:485-490. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 147] [Cited by in RCA: 158] [Article Influence: 10.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 8. | Wang Y, Sun CY, Scott L, Wu DD, Chen X. Texture and color enhancement imaging for detecting colorectal adenomas: Good, but not good enough. World J Gastrointest Endosc. 2022;14:471-473. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 9. | Toyoshima O, Nishizawa T, Yoshida S, Yamada T, Odawara N, Matsuno T, Obata M, Kurokawa K, Uekura C, Fujishiro M. Texture and color enhancement imaging in magnifying endoscopic evaluation of colorectal adenomas. World J Gastrointest Endosc. 2022;14:96-105. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in CrossRef: 15] [Cited by in RCA: 16] [Article Influence: 4.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 10. | Nishizawa T, Toyoshima O, Yoshida S, Uekura C, Kurokawa K, Munkhjargal M, Obata M, Yamada T, Fujishiro M, Ebinuma H, Suzuki H. TXI (Texture and Color Enhancement Imaging) for Serrated Colorectal Lesions. J Clin Med. 2021;11. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 20] [Cited by in RCA: 26] [Article Influence: 5.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 11. | Okimoto K, Matsumura T, Maruoka D, Kurosugi A, Shiratori W, Nagashima A, Ishikawa T, Kaneko T, Kanayama K, Akizue N, Ohta Y, Taida T, Saito K, Kato J, Kato N. Magnified endoscopy with texture and color enhanced imaging with indigo carmine for superficial nonampullary duodenal tumor: a pilot study. Sci Rep. 2022;12:10381. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in RCA: 8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 12. | Waki K, Kanesaka T, Michida T, Ishihara R, Tanaka Y. Improved visibility of early gastric cancer by using a combination of chromoendoscopy and texture and color enhancement imaging. Gastrointest Endosc. 2022;95:800-801. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 3] [Cited by in RCA: 4] [Article Influence: 1.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 13. | Nishizawa T, Yoshida S, Toyoshima A, Yamada T, Sakaguchi Y, Irako T, Ebinuma H, Kanai T, Koike K, Toyoshima O. Endoscopic diagnosis for colorectal sessile serrated lesions. World J Gastroenterol. 2021;27:1321-1329. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in CrossRef: 17] [Cited by in RCA: 18] [Article Influence: 3.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 14. | Sato T. TXI: Texture and Color Enhancement Imaging for Endoscopic Image Enhancement. J Healthc Eng. 2021;2021:5518948. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 59] [Cited by in RCA: 80] [Article Influence: 16.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 15. | Toyoshima O, Yoshida S, Nishizawa T, Yamakawa T, Sakitani K, Hata K, Takahashi Y, Fujishiro M, Watanabe H, Koike K. CF290 for pancolonic chromoendoscopy improved sessile serrated polyp detection and procedure time: a propensity score-matching study. Endosc Int Open. 2019;7:E987-E993. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 17] [Cited by in RCA: 20] [Article Influence: 2.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 16. | Yoshida S, Nishizawa T, Toyoshima O. Real-world clinical data of endoscopy-based cancer detection during the emergency declaration for COVID-19 in Japan. World J Gastrointest Endosc. 2020;12:401-403. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in CrossRef: 6] [Cited by in RCA: 5] [Article Influence: 0.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 17. | Suzuki T, Hara T, Kitagawa Y, Takashiro H, Nankinzan R, Sugita O, Yamaguchi T. Linked-color imaging improves endoscopic visibility of colorectal nongranular flat lesions. Gastrointest Endosc. 2017;86:692-697. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 61] [Cited by in RCA: 86] [Article Influence: 9.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 18. | Kobayashi S, Yamada M, Takamaru H, Sakamoto T, Matsuda T, Sekine S, Igarashi Y, Saito Y. Diagnostic yield of the Japan NBI Expert Team (JNET) classification for endoscopic diagnosis of superficial colorectal neoplasms in a large-scale clinical practice database. United European Gastroenterol J. 2019;7:914-923. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 30] [Cited by in RCA: 85] [Article Influence: 12.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 19. | The Paris endoscopic classification of superficial neoplastic lesions: esophagus, stomach, and colon: November 30 to December 1, 2002. Gastrointest Endosc. 2003;58:S3-43. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 1117] [Cited by in RCA: 1380] [Article Influence: 60.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (13)] |
| 20. | Yoshida N, Naito Y, Murakami T, Hirose R, Ogiso K, Inada Y, Dohi O, Kamada K, Uchiyama K, Handa O, Konishi H, Siah KTH, Yagi N, Fujita Y, Kishimoto M, Yanagisawa A, Itoh Y. Linked color imaging improves the visibility of colorectal polyps: a video study. Endosc Int Open. 2017;5:E518-E525. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 27] [Cited by in RCA: 30] [Article Influence: 3.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 21. | Suzuki S, Aniwan S, Chiu HM, Laohavichitra K, Chirapongsathorn S, Yamamura T, Kuo CY, Yoshida N, Ang TL, Takezawa T, Rerknimitr R, Ishikawa H, Gotoda T; ATLAS Trial Group. Linked-Color Imaging Detects More Colorectal Adenoma and Serrated Lesions: An International Randomized Controlled Trial. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2023;21:1493-1502.e4. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 28] [Cited by in RCA: 41] [Article Influence: 13.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 22. | Shinozaki S, Kobayashi Y, Hayashi Y, Sakamoto H, Sunada K, Lefor AK, Yamamoto H. Colon polyp detection using linked color imaging compared to white light imaging: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Dig Endosc. 2020;32:874-881. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 60] [Cited by in RCA: 63] [Article Influence: 10.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 23. | Ishikawa T, Matsumura T, Okimoto K, Nagashima A, Shiratori W, Kaneko T, Oura H, Tokunaga M, Akizue N, Ohta Y, Saito K, Arai M, Kato J, Kato N. Efficacy of Texture and Color Enhancement Imaging in visualizing gastric mucosal atrophy and gastric neoplasms. Sci Rep. 2021;11:6910. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 37] [Cited by in RCA: 43] [Article Influence: 8.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 24. | Singh R, Chiam KH, Leiria F, Pu LZCT, Choi KC, Militz M. Chromoendoscopy: role in modern endoscopic imaging. Transl Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020;5:39. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 18] [Cited by in RCA: 15] [Article Influence: 2.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 25. | Cellier C, Perrod G, Colas C, Dhooge M, Saurin JC, Lecomte T, Coron E, Rahmi G, Savale C, Chaussade S, Bellanger J, Dray X, Benech N, Le Rhun M, Barbieux JP, Pereira H, Chatellier G, Samaha E. Back-to-Back Comparison of Colonoscopy With Virtual Chromoendoscopy Using a Third-Generation Narrow-Band Imaging System to Chromoendoscopy With Indigo Carmine in Patients With Lynch Syndrome. Am J Gastroenterol. 2019;114:1665-1670. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 9] [Cited by in RCA: 12] [Article Influence: 1.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 26. | Lobo TF, Torloni MR, Mattar R, Nakamura MU, Alexandre SM, Daher S. Adipokine levels in overweight women with early-onset gestational diabetes mellitus. J Endocrinol Invest. 2019;42:149-156. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 15] [Cited by in RCA: 19] [Article Influence: 2.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
Open-Access: This article is an open-access article that was selected by an in-house editor and fully peer-reviewed by external reviewers. It is distributed in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial (CC BY-NC 4.0) license, which permits others to distribute, remix, adapt, build upon this work non-commercially, and license their derivative works on different terms, provided the original work is properly cited and the use is non-commercial. See: https://creativecommons.org/Licenses/by-nc/4.0/
Provenance and peer review: Unsolicited article; Externally peer reviewed.
Peer-review model: Single blind
Specialty type: Gastroenterology and hepatology
Country/Territory of origin: Japan
Peer-review report’s scientific quality classification
Grade A (Excellent): 0
Grade B (Very good): 0
Grade C (Good): C
Grade D (Fair): 0
Grade E (Poor): 0
P-Reviewer: Li XB, China S-Editor: Wang JJ L-Editor: A P-Editor: Wang JJ