Published online Sep 16, 2022. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v14.i9.547
Peer-review started: February 3, 2022
First decision: April 12, 2022
Revised: April 19, 2022
Accepted: August 6, 2022
Article in press: August 6, 2022
Published online: September 16, 2022
Processing time: 223 Days and 11.2 Hours
Endoscopic therapy using multiple plastic stents (MPSs) is the standard therapy for postorthotopic liver transplantation (p-OLT) anastomotic biliary stricture (AB
To evaluate the efficacy of endoscopic treatment using an Am-FCSEMS in patients with p-OLT ABS.
This study was conducted in a private tertiary care centre in São Paulo, Brazil and was approved by our institution's Human Research Committee. From April 2018 to October 2020, regardless of previous endoscopic treatment (MPS or FCSEMS), 17 patients with p-OLT ABS and indications for endoscopic therapy were in
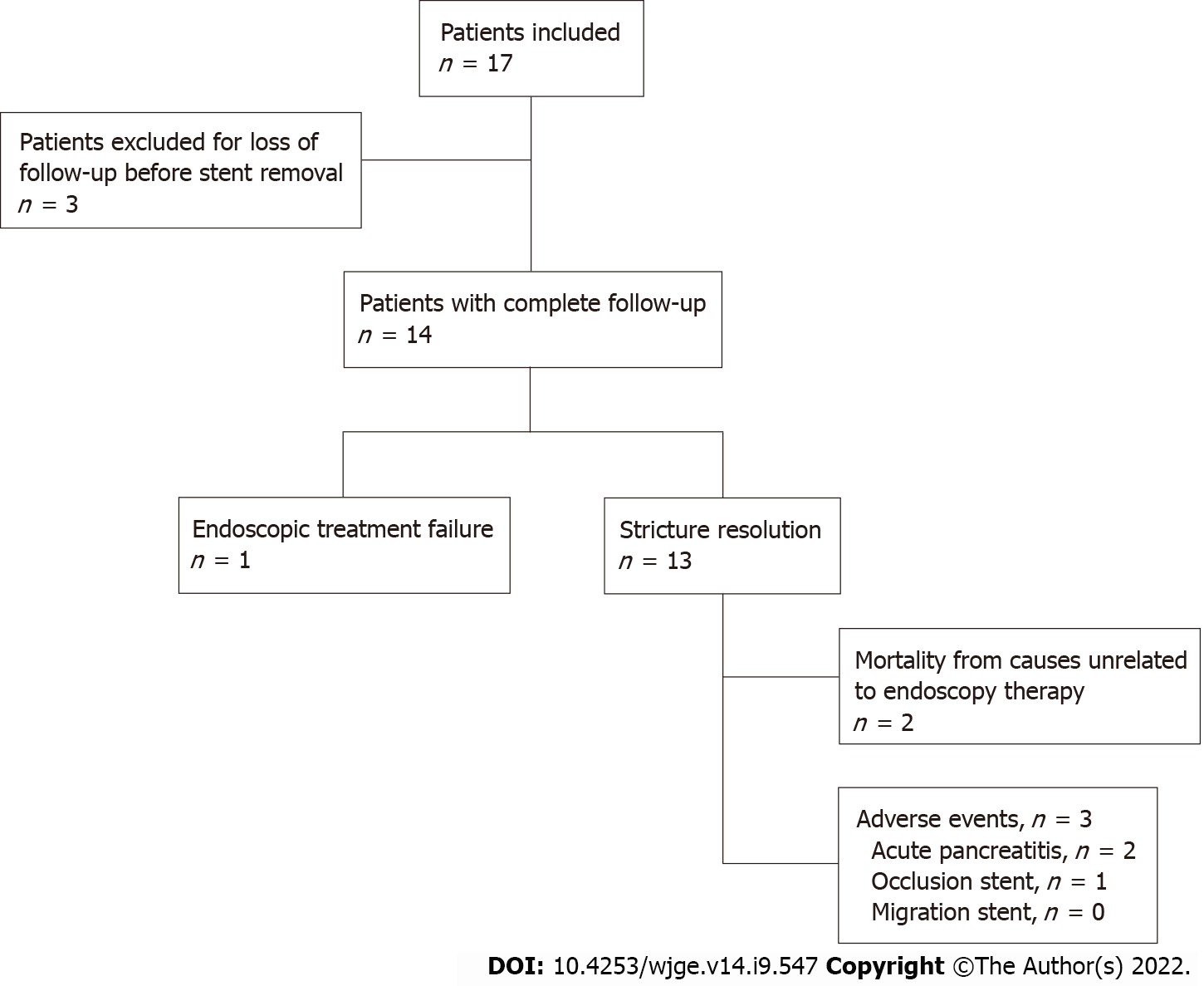
Three patients were excluded due to loss to follow-up before stent removal. Among the 14 patients included and followed, 7 were women, and the average age was 56 years (range: 28-76). The average period of Am-FCSEMS placement was 362 ± 109 d. Technical success occurred in all 14 patients (100%). There were no cases of distal stent migration. Complete resolution of the stricture occurred in 13/14 patients (92.85%). Adverse events occurred in 3/14 patients (21.42%): 2 patients with mild acute pancreatitis (14.28%) and 1 patient (7.14%) with stent dysfunction (occlusion by biliary sludge and stones, which was treated endoscopically without the need for stent removal). No deaths occurred related to therapy. All stents were removed using foreign body forceps or snares without difficulty. After Am-FCSEMS removal, all 13 patients who had ABS resolution were followed-up for an average of 411 ± 172 d, and there was no stricture recurrence or need for further endoscopic therapy.
In this retrospective study, endoscopy therapy using an Am-FCSEMS for p-OLT ABS was safe and effective, with a high stricture re
Core Tip: This retrospective study evaluated the efficacy of endoscopic treatment using an anti-migration fully covered self-expandable metallic stents (Am-FCSEMS) in patients with postorthotopic liver transplantation (p-OLT) anastomotic biliary stricture (ABS). Technical success occurred in all patients (100%). Stricture resolution occurred in 13/14 patients (92.85%). Adverse events occurred in 3/14 patients (21.42%). There were no cases of distal stent migration. After Am-FCSEMS removal, all 13 patients who had ABS resolution were followed-up for an average of 411 d, and there was no stricture recurrence or need for further endoscopic therapy. Endoscopic therapy using an Am-FCSEMS for p-OLT ABS is safe and effective, with a high stricture resolution rate, probably due to the absence of stent migration.
- Citation: Pinheiro LW, Martins FP, De Paulo GA, Contini MLC, Ferrari AP, Della Libera E. Endoscopic therapy using a self-expandable metallic stent with an anti-migration system for postorthotopic liver transplantation anastomotic biliary stricture. World J Gastrointest Endosc 2022; 14(9): 547-554
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5190/full/v14/i9/547.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4253/wjge.v14.i9.547
Biliary tract lesions are common postoperative adverse events (AEs) after orthotopic liver tran
Endoscopic balloon dilation followed by placement of side-by-side multiple plastic stents (MPSs) in repeated procedures every 3-4 mo, up to 12 mo, is the standard treatment for ABS. This treatment str
Despite such a high success rate, this strategy demands repeated procedures[1,6-9]. Recent studies using fully covered self-expandable metallic stents (FCSEMS) have shown encouraging results, with resolution rates similar to those observed with the MPS strategy[5,7,10]. However, a high FCSEMS migration rate of between 10% and 40% has been reported, which is a possible limitation for its use[5-7,10].
We hypothesized that a FCSEMS with an anti-migration system (Am-FCSEMS) could be an alte
The objective of this study was to evaluate the efficacy of endoscopic treatment using an Am-FCSEMS in patients with p-OLT ABS.
This study was conducted at Hospital Israelita Albert Einstein (HIAE), São Paulo, Brazil. HIAE is a pr
From April 2018 to October 2020, 17 patients between 18 and 76 years of age diagnosed with p-OLT ABS who were referred to the endoscopy unit were considered for inclusion in this retrospective study, regardless of previous endoscopic treatment (MPS or FCSEMS). The exclusion criteria were pregnancy, nonanastomotic biliary or hilar stricture, hepatic artery stenosis/thrombosis, isolated biliary fistulae, and patient refusal. To avoid the risk of biliary intrahepatic duct occlusion secondary to stent placement, a distance shorter than 2 cm from the stricture to the hepatic hilum was also considered an exclusion criterion.
This study was conducted in accordance with the World Medical Association Declaration of Helsinki Ethical Principles for Medical Research Involving Human Subjects and was approved by our in
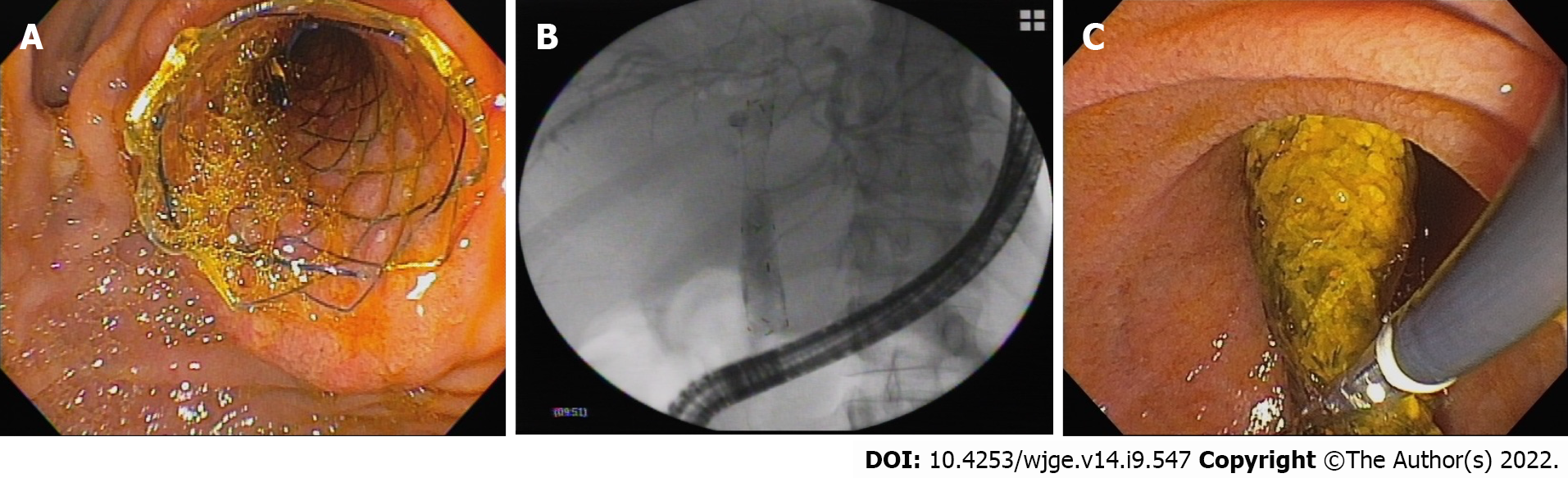
Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) was performed using a therapeutic video duodenoscope (TJF-180 Olympus Optical Co., Ltd., Tokyo, Japan) with patients under monitored anaesthesia. After selective biliary cannulation, cholangiography was performed for the evaluation and characterization of biliary stricture, followed by the passage of a guidewire. After positioning the guidewire, biliary sphincterotomy was performed in patients with native papilla, and an Am-FCSEMS (10 mm in final diameter and 60 or 80 mm in length, BCT HanarostentTM M.I. Tech, Co.) was placed (Figure 1A and B). Balloon dilation of the stricture was performed only if necessary to introduce the stent. According to the physician’s choice, the length of the stent was determined during cholangiography to place the proximal end between the stricture and the hepatic hilum and the distal end in the duodenum. Patients were followed up for clinical signs of biliary obstruction and scheduled to have the stent removed after 12 mo if no complications occurred.
The primary study endpoint was the efficacy of the endoscopic treatment of p-OLT ABS using an Am-FCSEMS for a 12-mo period. Efficacy was evaluated based on ABS resolution. After stent removal, the biliary stricture was considered resolved if there was no stricture observed on cholangiography or a minimum stricture that allowed the passage of a 12-mm inflated extractor balloon without difficulty. Secondary endpoints were technical success (defined as stent placement), adverse effects related to ERCP (bleeding or pancreatitis), and stent dysfunction (migration or obstruction).
A total of 17 patients were included. Three patients were excluded due to loss to follow-up before stent removal (12 mo) (Figure 2). The average age of the 14 patients included and followed was 56 years (range: 28-76); 7 women had an average age of 42 ± 11.2 years, and 7 men had an average age of 69 ± 5.8 years. Patient characteristics are shown in Table 1. Among the 14 patients, 8 (57.14%) had already undergone treatment with FCSEMS and/or MPSs, but endoscopic management was considered unsuccessful, with an average number of procedures before inclusion in this study of 2.25 ± 1.04 (range: 1-4). The other 6 patients (42.85%) received an Am-FCSEMS as the first treatment. Regardless of previous treatment, the average interval from p-OLT to the first ERCP was 116 wk (range: 4-570). The average duration of placement of an Am-FCSEMS in this study was 362 ± 109 d (range: 226-609). The length of stent placement was 6 cm in 8 patients and 8 cm in 6 patients. Technical success (stent placement) occurred in all 14 patients (100%). The clinical follow-up after stent removal was 411 ± 172 d (range: 55-692). All stents were removed using foreign body forceps or snares without any technical difficulty (Figure 1C).
| Overall patient characteristics | Results |
| No. of patients, n | 14 |
| Gender, female sex, n (%) | 7 (50) |
| Age (yr), mean (range) | 56 (28-76) |
| Cause of liver transplant: n | |
| HBV | 2 |
| HBV + HCV | 1 |
| Alcohol | 3 |
| Cryptogenic | 2 |
| NASH | 1 |
| Autoimmune hepatitis | 2 |
| Primary biliary cirrhosis | 1 |
| Familial amyloidosis | 1 |
| Primary hyperoxaluria | 1 |
| Presence of HCC: n | 4 |
| Time from OLT to ERCP (wk) | |
| mean ± SD | 116 ± 156 |
| Median | 45 |
| Range | 4-570 |
| Patients with previous endoscopic treatment before Am-FCSEMS, n (%) | 8 (57.14) |
| Procedures before Am-FCSEMS (mean) | 2.25 |
| Patients with no previous endoscopic treatment, n (%) | 6 (42.86) |
Complete resolution of the stricture occurred in 13/14 patients (92.85%). Only 1 patient (7.14%) experienced endoscopic treatment failure after 338 d with the stent in place, which was determined by cholangiography as persistence of stricture. This patient was referred for endoscopic treatment using MPSs for a longer period. AEs occurred in 3 out of 14 patients (21.42%). There were 2 patients (14.28%) with mild acute pancreatitis and 1 patient (7.14%) with stent dysfunction (occlusion by biliary sludge and stones with cholangitis), which was treated endoscopically without the need for stent removal. There was no distal migration of the stent in any patient (Table 2). There was no mortality related to ERCP and/or endoscopic therapy with the stent. After removal of the Am-FCSEMS, all 13 patients who had ABS resolution were followed-up (411 ± 172 d), and there was no need for further endoscopic therapy or stricture recurrence. Two patients died from causes unrelated to endoscopy therapy.
| Overall results | |
| No. of patients, n | 14 |
| Technical success, n (%) | 14 (100) |
| Stricture resolution, n (%) | 13 (92.85) |
| Treatment failure, n (%) | 1 (7.14) |
| Mean ALT before stent (U/L) | 144 |
| Mean ALT at the end of follow-up (U/L) | 16 |
| Mean total bilirubin before stent (mg/dL) | 1. 88 |
| Mean total bilirubin at the end of follow-up (mg/dL) | 0. 49 |
| Stricture recurrence, n | 0 |
| Stent migration | 0 |
| Other complications, n (%) | 3 (21.42) |
| Acute pancreatitis | 2 (14.28) |
| Stent occlusion | 1 (7.14) |
| Mean follow-up after stent removal (d) | 411 ± 172 |
Our present study shows that p-OLT ABS treatment with an Am-FCSEMS is effective and safe, with a stricture resolution rate of 92.85%, which is comparable to the results of other studies involving MPSs[5,9,12] and FCSEMSs[5,7,13]. In our study, the average time between liver transplantation and endoscopy therapy for ABS was lengthy (116 wk), which may have impacted the results and thus, is a possible limitation of this study[3,6,8]. Nevertheless, our results were comparable with those of other studies that used this anti-migration stent model[11].
The longer stent maintenance period (12 mo) in our study in relation to other studies with metallic stents[2,7] and the absence of migration possibly related to the antimigration mechanism may have contributed to the favourable result observed in our patients.
The technical success rate of 100% in this series, which is comparable to that in other studies[6,12,14], demonstrates the applicability of this technique. No patients experienced distal migration of the stent. As described in previous studies, the main disadvantage of using FCSEMS is the high migration rate of up to 37.5%[10,12,14,15]. It is possible that treatment with an Am-FCSEMS may present better results due to the lower risk of migration and longer stent patency. Although in our study assessment of costs was not an included objective, it is possible that since this stent has a lower migration rate its use could result in a lower number of procedures and thus lower costs, but this hypothesis should be verified in future controlled studies.
The AEs observed with ERCP-related therapy and/or stenting were mild pancreatitis and delayed stent obstruction. All patients in whom the stent was placed underwent biliary sphincterotomy, and mild acute pancreatitis was related to the ERCP procedure in 2 out of the 14 patients (14.2%). Despite this higher rate of complications compared to that in the literature[5-7,13], these patients underwent successful clinical treatment. Stent dysfunction (obstruction) occurred late and was caused by biliary sludge or stones, with jaundice and cholangitis occurring in only one patient (7.1%). This complication and its endoscopic treatment with or without stent replacement is described in the literature[5,6]. This patient was treated with antibiotics and endoscopy without the need for stent replacement.
No complications occurred during stent removal. In this study, no serious complications or deaths related to endoscopic treatment were reported. The average follow-up of patients who had stricture resolution after removal of the metallic stent was 411 d. There was no ABS recurrence during follow-up. This positive result may be related to the prolonged maintenance of the metallic stent, which was longer than 6 mo[2,5].
Considering the treatment of patients with p-OLT ABS, the use of FCSEMSs may be an interesting alternative in relation to MPS therapy, considering FCSEMS placement presents comparable results with fewer ERCP procedures[4,5,7,10]. However, spontaneous stent migration may be a limitation of FCSEMS placement[10,12,14].
This retrospective study has some limitations, such as a small sample size from a single centre. Another limiting point for this study is the lack of a control group. However, our results showed that treatment with Am-FCSEMS can be an alternative for patients with p-OLT ABS. Therefore, prospective and comparative studies should be encouraged to evaluate the efficacy of endoscopic treatment using Am-FCSEMS versus MPSs. Nevertheless, we present similar results for the resolution of ABS compared to those in other studies using MPSs and FCSEMSs as well as a recent study using an Am-FCSEMS. In this series, the advantage of treatment using an Am-FCSEMS in relation to treatment with MPSs was the need for only two ERCP procedures over 12 mo, while the advantage in relation to FCSEMS therapy was the absence of migration.
In conclusion, in this retrospective study, endoscopy therapy using an Am-FCSEMS or flaps for p-OLT ABS is safe and effective, with the stricture´s high-resolution rate probably being due to the absence of stent migration.
Endoscopic therapy using multiple plastic stents is the standard therapy for postorthotopic liver transplantation (p-OLT) anastomotic biliary stricture (ABS). However, this approach demands repeated procedures. Recent studies using fully covered self-expandable metallic stents (FCSEMS) have shown encouraging results, but migration occurs in 10% to 40% of cases. We hypothesized that a FCSEMS with an anti-migration system (Am-FCSEMS) could be an alternative for treatment in patients with p-OLT ABS.
The efficacy of treatment using an Am-FCSEMS for p-OLT ABS is not yet well established. The outcomes of endoscopic treatment using this type of stent have become clinically relevant.
This study aimed to evaluate the efficacy of endoscopic treatment using an Am-FCSEMS in patients with p-OLT ABS.
This study was conducted in a private tertiary care centre in São Paulo, Brazil. From April 2018 to October 2020, patients with p-OLT ABS and indications for endoscopic therapy were included in this study, and an Am-FCSEMS (10 mm in final diameter and 60 or 80 mm in length) was placed (Hanarostent MI Tech, Co).
Technical success occurred in all 14 patients (100%). There were no cases of distal stent migration. Complete resolution of the stricture occurred in 13/14 patients (92.85%). Adverse events occurred in 3/14 patients (21.42%): 2 patients with mild acute pancreatitis and 1 patient with stent dysfunction (occlusion). No deaths occurred related to therapy. After Am-FCSEMS removal, all 13 patients who had ABS resolution were followed-up for an average of 411 ± 172 d, and there was no stricture recurrence or need for further endoscopic therapy.
Endoscopy therapy using an Am-FCSEMS for p-OLT ABS is safe and effective, with the stricture´s high-resolution rate probably being due to the absence of stent migration.
This study shows that treatment using Am-FCSEMS has a high rate of stenosis resolution, probably due to the absence of stent migration, and may result in a lower number of procedures.
| 1. | Williams ED, Draganov PV. Endoscopic management of biliary strictures after liver transplantation. World J Gastroenterol. 2009;15:3725-3733. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in CrossRef: 78] [Cited by in RCA: 85] [Article Influence: 5.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 2. | Thuluvath PJ, Pfau PR, Kimmey MB, Ginsberg GG. Biliary complications after liver transplantation: the role of endoscopy. Endoscopy. 2005;37:857-863. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 157] [Cited by in RCA: 154] [Article Influence: 7.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 3. | Pascher A, Neuhaus P. Biliary complications after deceased-donor orthotopic liver transplantation. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg. 2006;13:487-496. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 105] [Cited by in RCA: 105] [Article Influence: 5.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 4. | Ryu CH, Lee SK. Biliary strictures after liver transplantation. Gut Liver. 2011;5:133-142. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 98] [Cited by in RCA: 113] [Article Influence: 7.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 5. | Coté GA, Slivka A, Tarnasky P, Mullady DK, Elmunzer BJ, Elta G, Fogel E, Lehman G, McHenry L, Romagnuolo J, Menon S, Siddiqui UD, Watkins J, Lynch S, Denski C, Xu H, Sherman S. Effect of Covered Metallic Stents Compared With Plastic Stents on Benign Biliary Stricture Resolution: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA. 2016;315:1250-1257. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 158] [Cited by in RCA: 174] [Article Influence: 17.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 6. | Devière J, Nageshwar Reddy D, Püspök A, Ponchon T, Bruno MJ, Bourke MJ, Neuhaus H, Roy A, González-Huix Lladó F, Barkun AN, Kortan PP, Navarrete C, Peetermans J, Blero D, Lakhtakia S, Dolak W, Lepilliez V, Poley JW, Tringali A, Costamagna G; Benign Biliary Stenoses Working Group. Successful management of benign biliary strictures with fully covered self-expanding metal stents. Gastroenterology. 2014;147:385-95; quiz e15. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 171] [Cited by in RCA: 174] [Article Influence: 14.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 7. | Martins FP, De Paulo GA, Contini MLC, Ferrari AP. Metal versus plastic stents for anastomotic biliary strictures after liver transplantation: a randomized controlled trial. Gastrointest Endosc. 2018;87:131.e1-131.e13. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 65] [Cited by in RCA: 92] [Article Influence: 11.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 8. | Sharma S, Gurakar A, Jabbour N. Biliary strictures following liver transplantation: past, present and preventive strategies. Liver Transpl. 2008;14:759-769. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 263] [Cited by in RCA: 281] [Article Influence: 15.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (4)] |
| 9. | Krok KL, Cárdenas A, Thuluvath PJ. Endoscopic management of biliary complications after liver transplantation. Clin Liver Dis. 2010;14:359-371. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 37] [Cited by in RCA: 35] [Article Influence: 2.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 10. | Jiménez-Pérez M, Melgar Simón JM, Durán Campos A, González Grande R, Rodrigo López JM, Manteca González R. Endoscopic Management of Post-Liver Transplantation Biliary Strictures With the Use of Fully Covered Metallic Stents. Transplant Proc. 2016;48:2510-2514. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 12] [Cited by in RCA: 14] [Article Influence: 1.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 11. | Bordaçahar B, Perdigao F, Leblanc S, Barret M, Duchmann JC, Guillaumot MA, Chaussade S, Scatton O, Prat F. Clinical efficacy of anti-migration features in fully covered metallic stents for anastomotic biliary strictures after liver transplantation: comparison of conventional and anti-migration stents. Gastrointest Endosc. 2018;88:655-664. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 16] [Cited by in RCA: 24] [Article Influence: 3.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 12. | García-Pajares F, Sánchez-Antolín G, Pelayo SL, Gómez de la Cuesta S, Herranz Bachiller MT, Pérez-Miranda M, de La Serna C, Vallecillo Sande MA, Alcaide N, Llames RV, Pacheco D, Caro-Patón A. Covered metal stents for the treatment of biliary complications after orthotopic liver transplantation. Transplant Proc. 2010;42:2966-2969. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 46] [Cited by in RCA: 46] [Article Influence: 2.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 13. | Kahaleh M, Behm B, Clarke BW, Brock A, Shami VM, De La Rue SA, Sundaram V, Tokar J, Adams RB, Yeaton P. Temporary placement of covered self-expandable metal stents in benign biliary strictures: a new paradigm? Gastrointest Endosc. 2008;67:446-454. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 182] [Cited by in RCA: 165] [Article Influence: 9.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 14. | Traina M, Tarantino I, Barresi L, Volpes R, Gruttadauria S, Petridis I, Gridelli B. Efficacy and safety of fully covered self-expandable metallic stents in biliary complications after liver transplantation: a preliminary study. Liver Transpl. 2009;15:1493-1498. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 103] [Cited by in RCA: 103] [Article Influence: 6.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 15. | Tarantino I, Traina M, Mocciaro F, Barresi L, Curcio G, Di Pisa M, Granata A, Volpes R, Gridelli B. Fully covered metallic stents in biliary stenosis after orthotopic liver transplantation. Endoscopy. 2012;44:246-250. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 53] [Cited by in RCA: 54] [Article Influence: 3.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
Conflict of interest statement: Dr. De Paulo GA and Dr. Ferrari AP are the medical consultant for Boston Scientific and Olympus. The remaining authors have no conflicting relationships to disclose.
Open-Access: This article is an open-access article that was selected by an in-house editor and fully peer-reviewed by external reviewers. It is distributed in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial (CC BY-NC 4.0) licence, which permits others to distribute, remix, adapt, and build upon this work noncommercially and licence their derivative works on different terms, provided the original work is properly cited and the use is noncommercial. See https://creativecommons.org/Licenses/by-nc/4.0/
Provenance and peer review: Unsolicited article; Externally peer reviewed.
Peer-review model: Single blind
Specialty type: Gastroenterology and hepatology
Country/Territory of origin: Brazil
Peer-review report’s scientific quality classification
Grade A (Excellent): 0
Grade B (Very good): 0
Grade C (Good): C, C
Grade D (Fair): D
Grade E (Poor): 0
P-Reviewer: Ferrarese A, Italy; Lynch EN, Italy S-Editor: Yan JP L-Editor: A P-Editor: Yan JP