©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastrointest Endosc. Oct 16, 2017; 9(10): 535-539
Published online Oct 16, 2017. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v9.i10.535
Published online Oct 16, 2017. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v9.i10.535
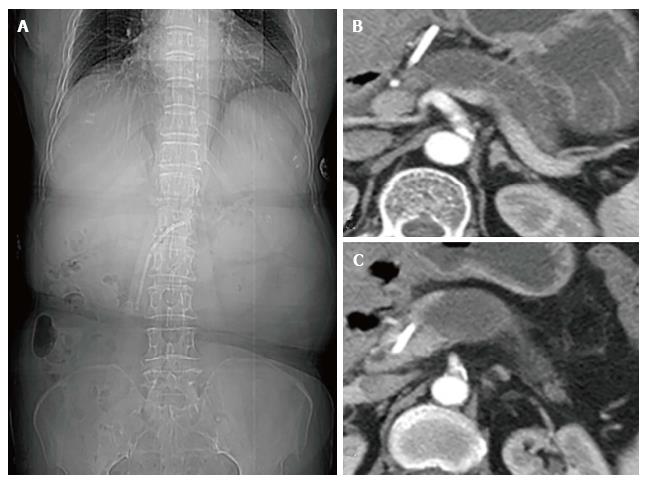
Figure 1 Abdominal computed tomography.
A: Computed tomography image showing a pancreatic stent; B and C: An endoprosthesis extending from the main pancreatic duct (MPD) and parenchyma into the lesser omental bursa with a dilated distal MPD.
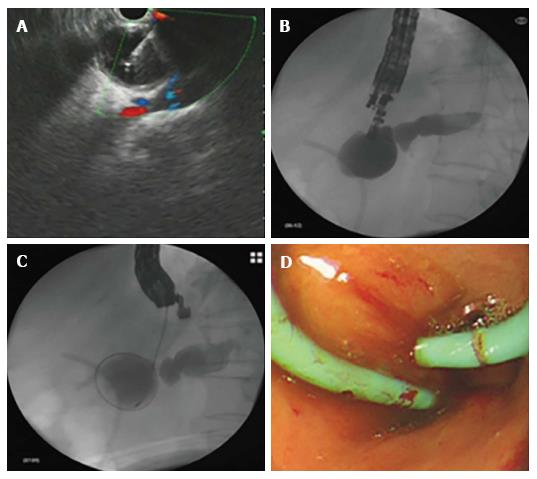
Figure 2 Endoscopic ultrasound-guided pancreaticogastrostomy.
A: Endoscopic ultrasound-guided puncture; B and C: Contrast injection and cystotome advancement; D: Double pigtail stent placement.
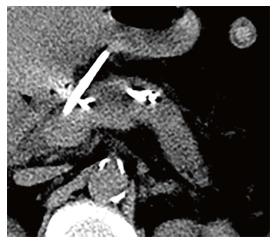
Figure 3 Successful decompression of the dilated main pancreatic duct.
- Citation: Lu L, Jin HB, Yang JF, Zhang XF. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided pancreaticogastrostomy for symptomatic pancreatic duct obstruction caused by migrated pancreatic stent. World J Gastrointest Endosc 2017; 9(10): 535-539
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5190/full/v9/i10/535.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4253/wjge.v9.i10.535