©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastrointest Endosc. Oct 25, 2015; 7(15): 1157-1169
Published online Oct 25, 2015. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v7.i15.1157
Published online Oct 25, 2015. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v7.i15.1157
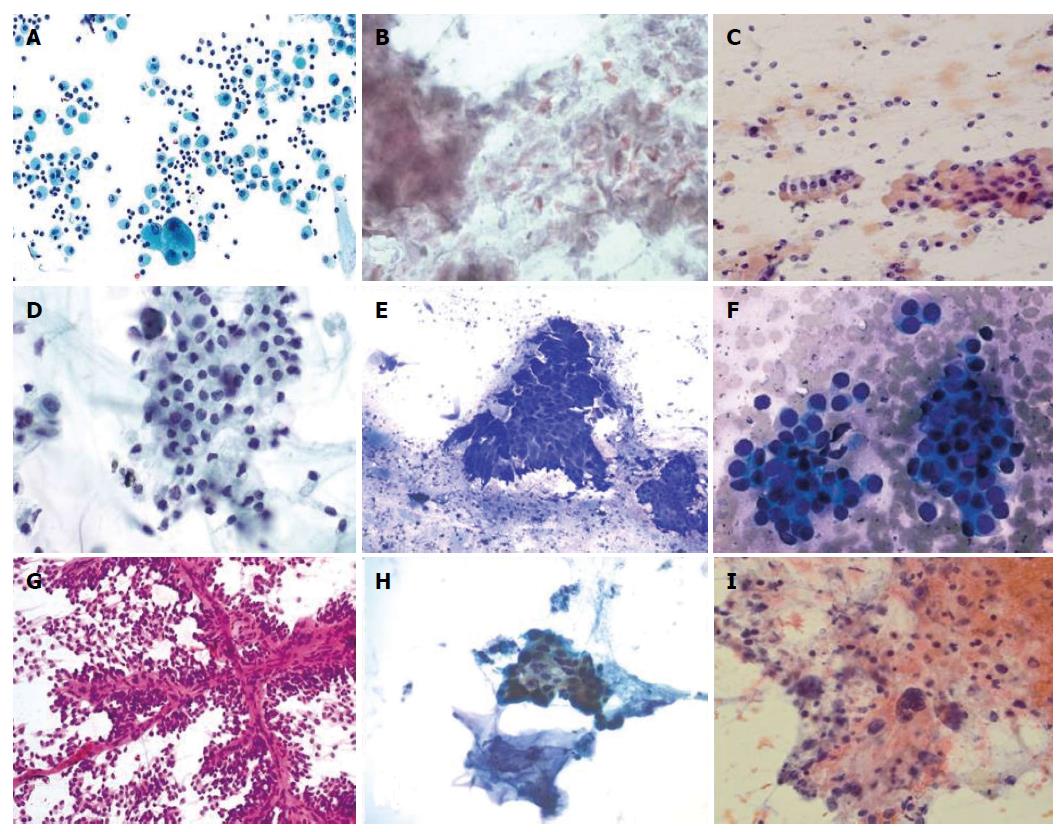
Figure 1 Cytopathologic features of pancreatic cysts.
A: Pseudocyst: Notice the macrophages and inflammatory cells; epithelial cells are not seen; B: Lymphoepithelial cyst: Numerous anucleated squamous cells and keratinized debris are seen; C: Serous cystadenoma: One group of bland, monomorphic epithelial cells is present along with background histiocytes; D: Mucinous cystic neoplasm: A sheet of columnar cells with low-grad dysplasia in the background of mucin; E: Intraductal papillary neoplasm: Large papillary clusters are lined by tall, columnar cells containing intracytoplasmic mucin in the background extracellular mucin; F: Pancreatic neuroendocrine neoplasm: Bland, monomorphic epithelial cells with eccentrically placed nuclei arranged singly and in clusters characterizes this lesion; G: Solid pseudopapillary neoplasm: Notice the delicate, branching vessels and the poorly cohesive, bland epithelial cells; H: Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma with mucinous cyst: The ductal cells are arranged haphazardly and are characterized by hyperchromasia, nuclear pleomorphism and irregular nuclear contour; I: Undifferentiated carcinoma with osteoclast-like giant cells and mucinous cystic neoplasm: Multiple osteoclast-like giant cells and large haphazardly nucleus in the background of mucin.
- Citation: Martin AK, Zhou Z. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration for the diagnosis of pancreatic cysts by combined cytopathology and cystic content analysis. World J Gastrointest Endosc 2015; 7(15): 1157-1169
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5190/full/v7/i15/1157.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4253/wjge.v7.i15.1157