©2012 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastrointest Endosc. Nov 16, 2012; 4(11): 479-488
Published online Nov 16, 2012. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v4.i11.479
Published online Nov 16, 2012. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v4.i11.479
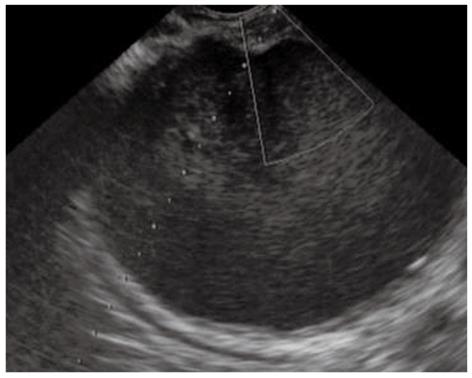
Figure 1 Ultrasonographic image of the pancreatic fluid collection to identify an appropriate puncture route which has no interposing vessels.
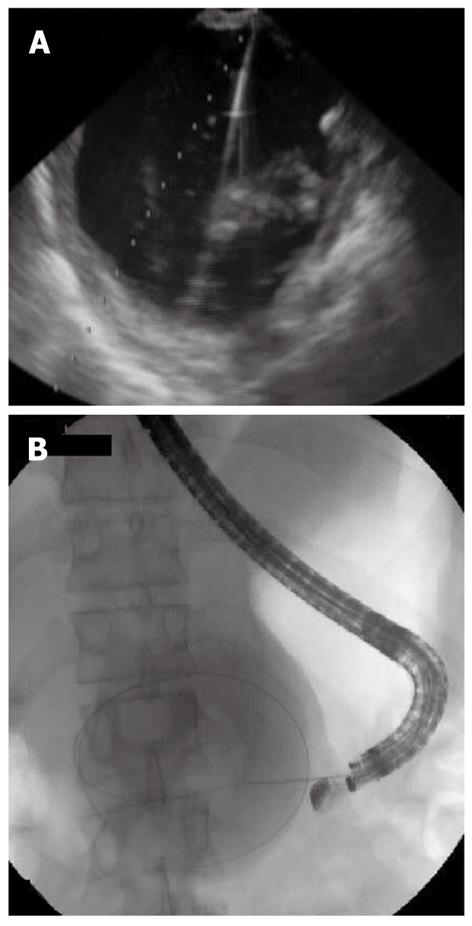
Figure 2 Needle puncture of the pancreatic fluid collection and insertion of a guide-wire.
A: Ultrasonographic image of needle puncture of the pancreatic fluid collection; B: Radiological image of insertion of a guide-wire in the pancreatic fluid collection.
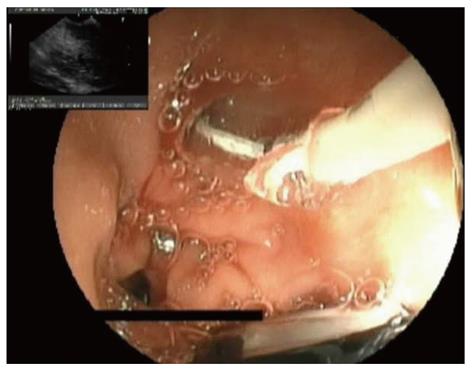
Figure 3 Dilation of the punctured tract, creating a fistula between gut wall and the pancreatic fluid collection.
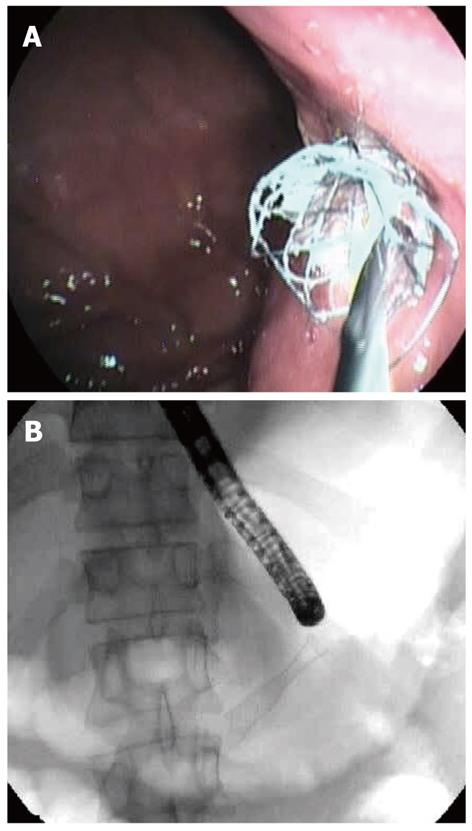
Figure 4 Insertion of the drainage tubes.
A: Endoscopic image of insertion of a fully covered self-expanding metal stent; B: Radiological image of insertion of a fully covered self-expanding metal stent.
- Citation: Fabbri C, Luigiano C, Maimone A, Polifemo AM, Tarantino I, Cennamo V. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided drainage of pancreatic fluid collections. World J Gastrointest Endosc 2012; 4(11): 479-488
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5190/full/v4/i11/479.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4253/wjge.v4.i11.479