©2011 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastrointestinal Endoscopy. Oct 16, 2011; 3(10): 183-194
Published online Oct 16, 2011. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v3.i10.183
Published online Oct 16, 2011. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v3.i10.183
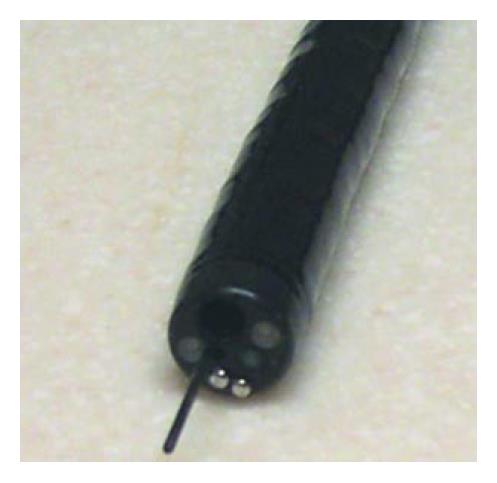
Figure 1 Image of fiber bundle extending through the biopsy port of a standard white-light endoscope[7].
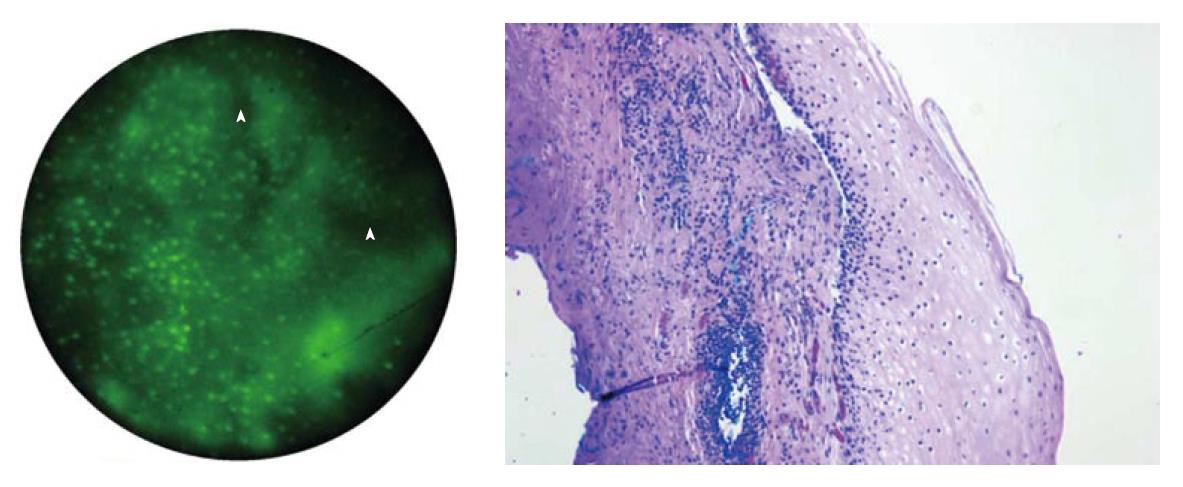
Figure 2 Images of normal squamous tissue using the High Resolution Microendoscope.
A: Endoscopic microscope image of normal squamous tissue stained with 0.05% acriflavine shows flat arrangement of squamous epithelium with round regularly spaced nuclei. The round clear spaces surrounded by the epithelium represent the papillae (arrowhead). The acriflavine in image A highlights the nuclei; B: Histopathology of same specimen. Scale bar is 100 microns.
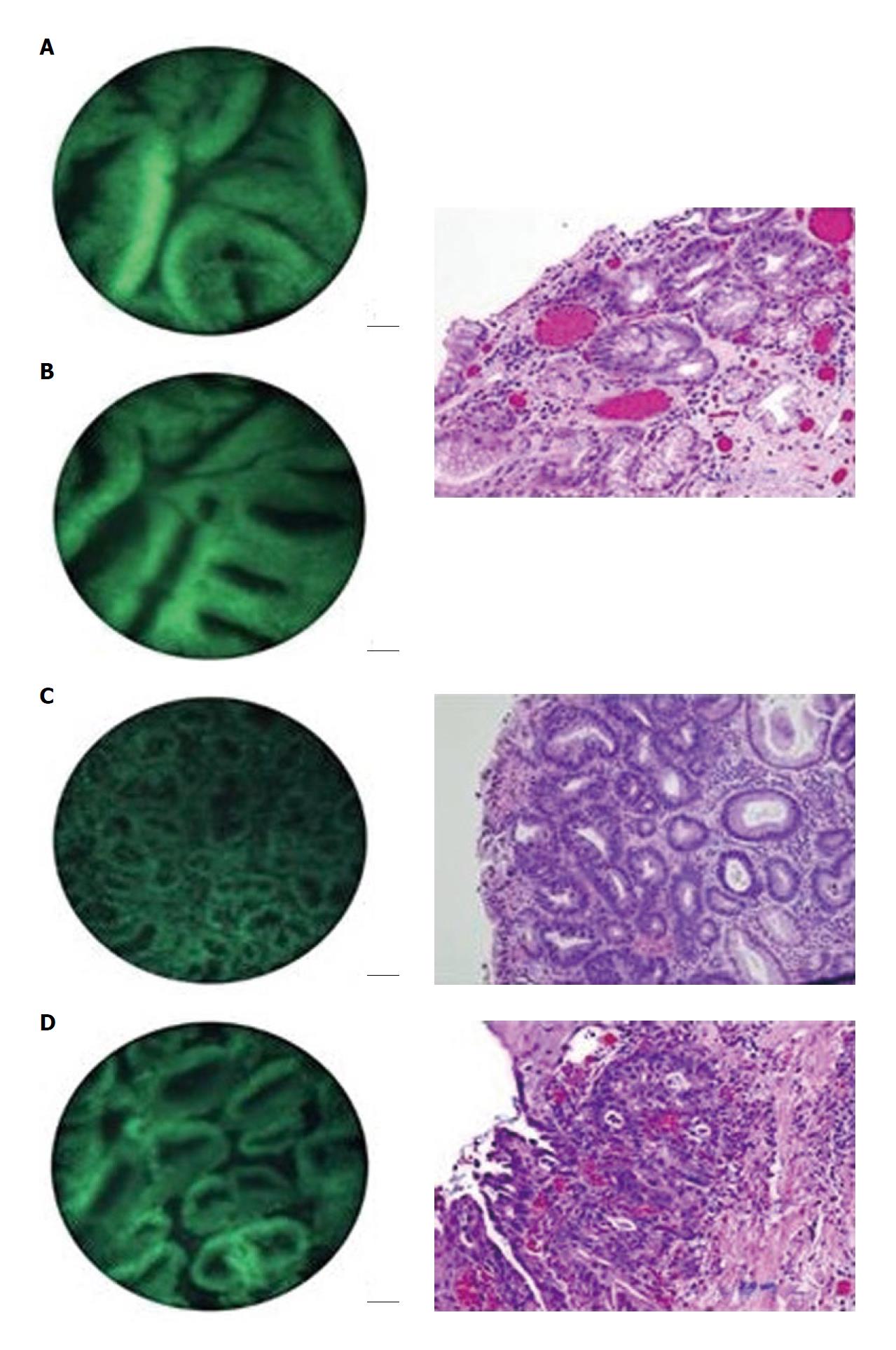
Figure 3 High resolution microendoscope in Barrett’s esophagus: After staining with topical acriflavine, corresponding microendoscopic and histopathological images are shown of Barrett’s metaplasia/LGD (A, B) and high grade dysplasia (C, D).
The uniformly shaped and spaced glands with intact nuclear polarity can easily be differentiated from the crowded, back-to-back glandular architecture noted in HGD.
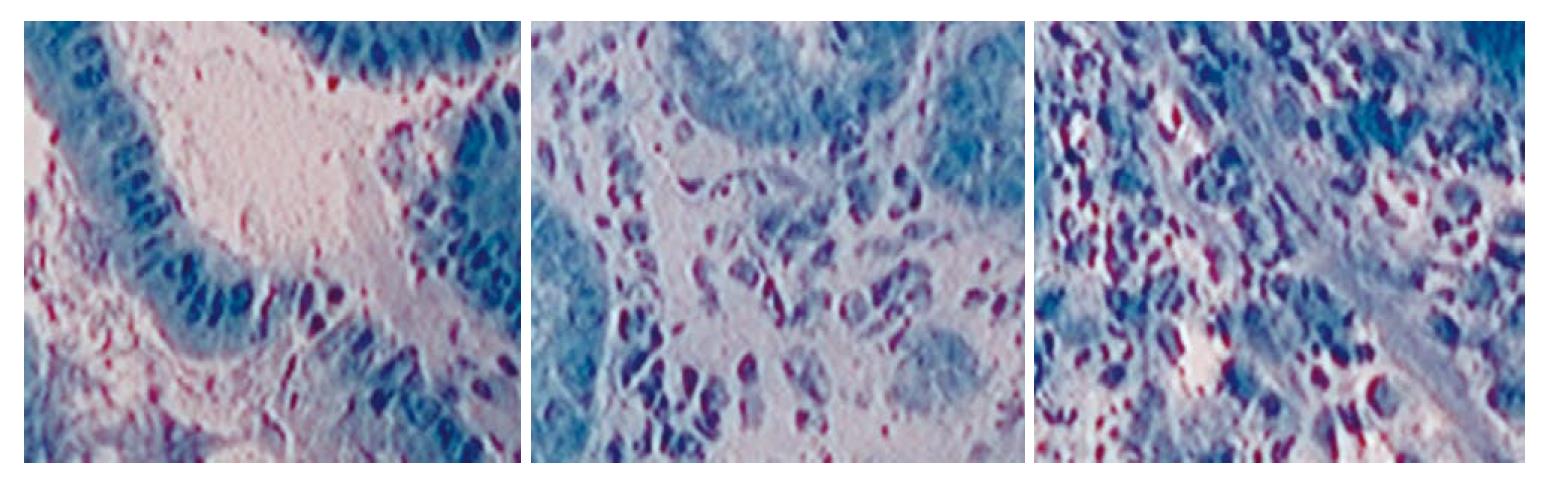
Figure 4 Endocytoscopy enables visualization of different cytological and architectural features, including size, arrangement and density of cells (adapted with permissionp[51]).
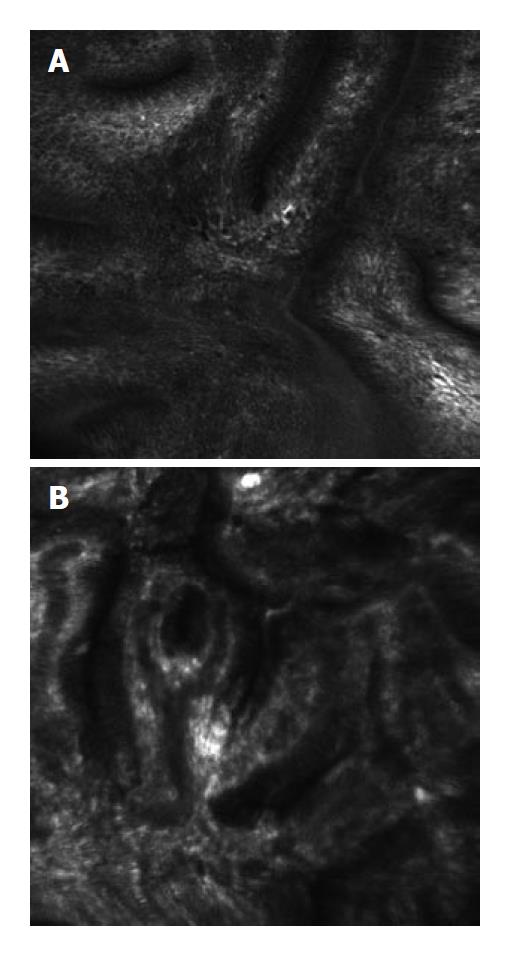
Figure 5 Confocal laser endoscopy image of Barrett’s metaplasia (A) and high grade dysplasia (HGD) (B) after the intravenous administration of 5 mL of intravenous fluorescein as an exogenous contrast agent.
The fluorescein enhances the subepithelial capillary network. HGD can be distinguished from non-neoplastic Barrett's esophagus by the branching, irregular capillary network and irregular, thickened basement membrane.
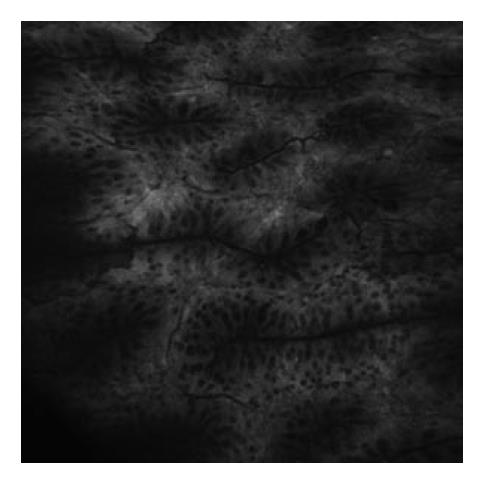
Figure 6 Normal colonic mucosa seen with a confocal endomicroscope.
Glands are seen longitudinally but are well organized and homogenous. Goblet cells appear black.
- Citation: Shukla R, Abidi WM, Richards-Kortum R, Anandasabapathy S. Endoscopic imaging: How far are we from real-time histology? World J Gastrointestinal Endoscopy 2011; 3(10): 183-194
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5190/full/v3/i10/183.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4253/wjge.v3.i10.183