©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastrointest Endosc. Dec 16, 2025; 17(12): 110136
Published online Dec 16, 2025. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v17.i12.110136
Published online Dec 16, 2025. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v17.i12.110136
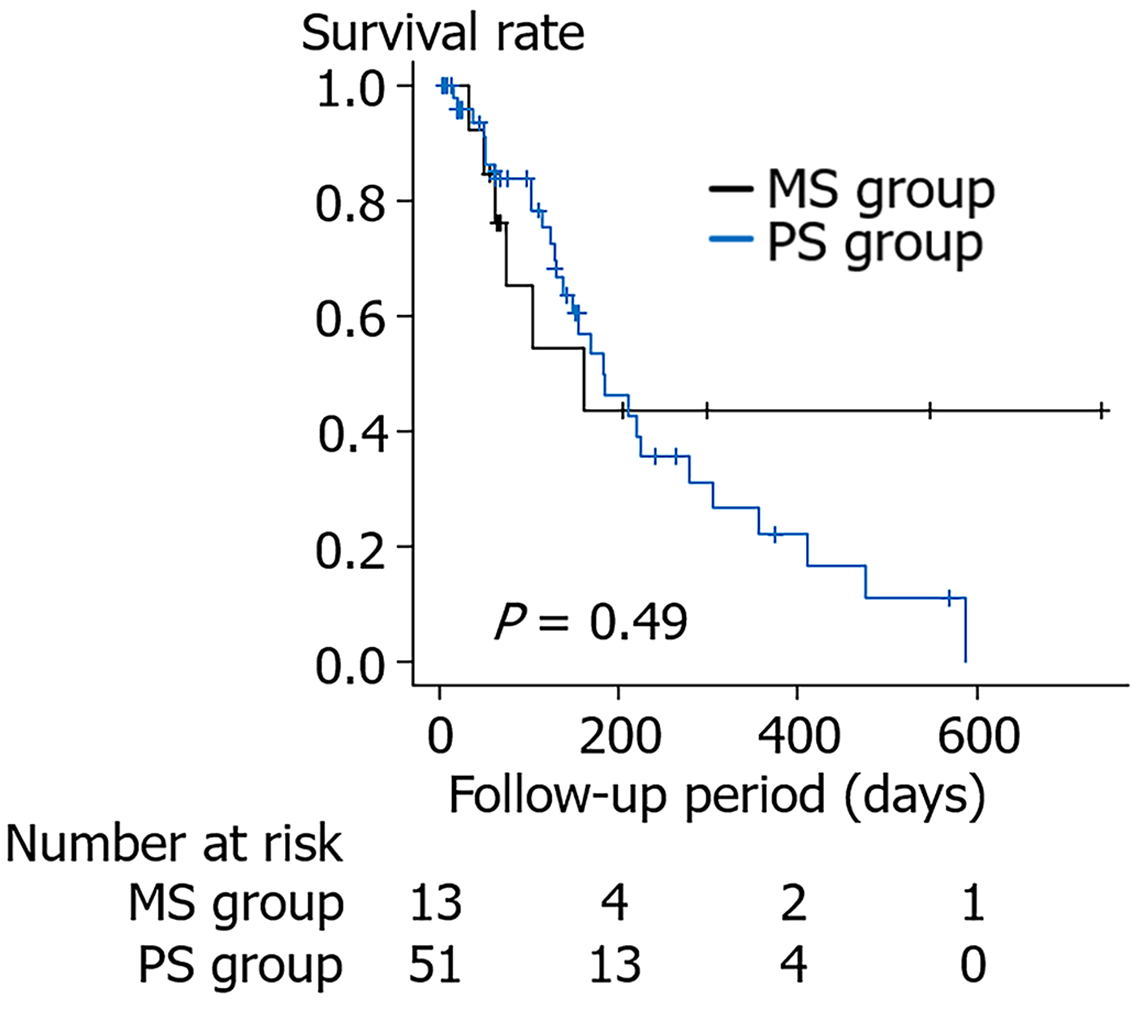
Figure 1 Comparison of the follow-up duration between the two groups.
MS: Metallic stent; PS: Plastic stent.
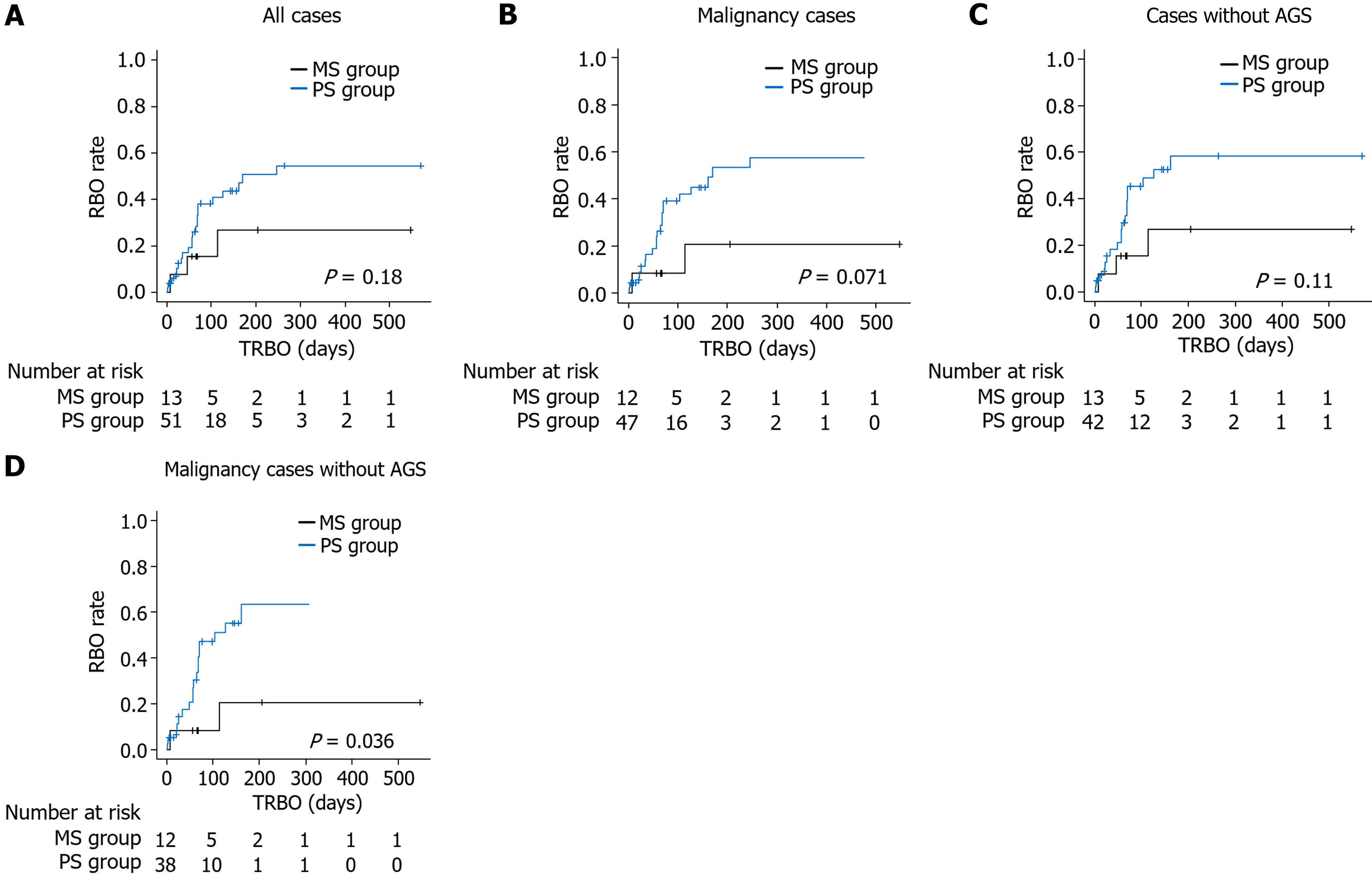
Figure 2 Comparison of the time to recurrent biliary obstruction between the metallic stent group and the plastic stent group.
A: All patients; B: Patients with malignancy; C: Patients without antegrade stenting; D: Patients with malignancy without antegrade stenting. RBO: Recurrent biliary obstruction; MS: Metallic stent; PS: Plastic stent; TRBO: Time to recurrent biliary obstruction; AGS: Antegrade stenting.
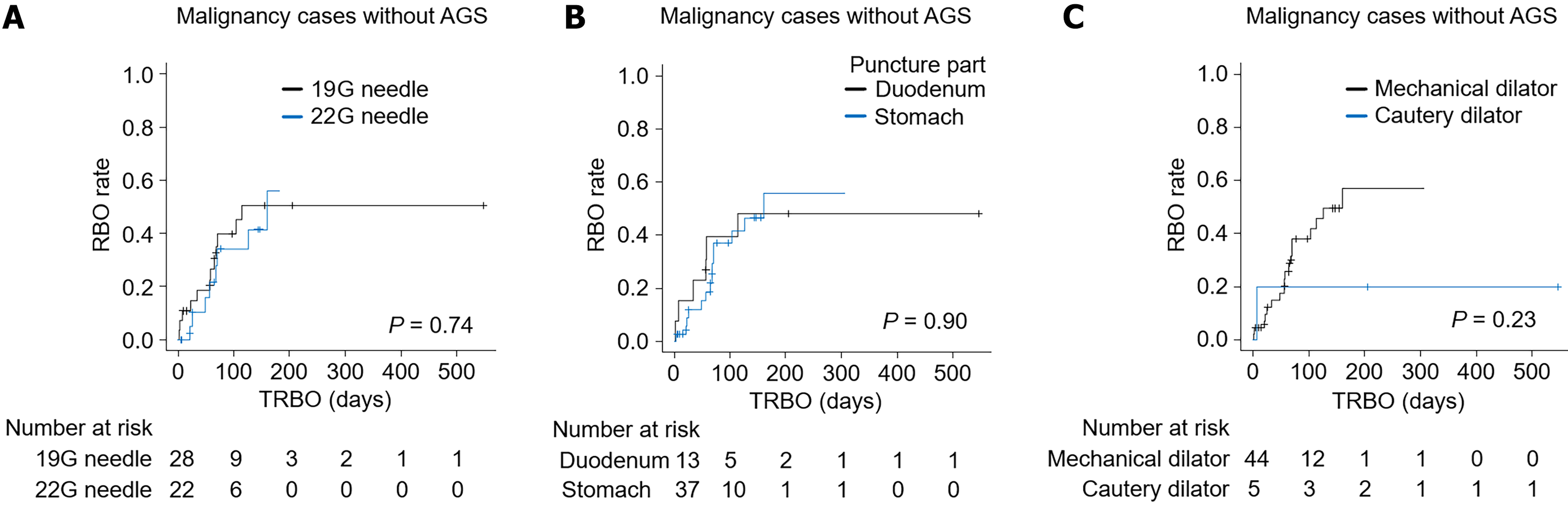
Figure 3 Comparison of the time to recurrent biliary obstruction in patients with malignancy without antegrade stenting.
A: Needle gauge (19-gauge vs 22-gauge); B: Puncture location (duodenum vs stomach); C: Dilator type (mechanical vs cautery). AGS: Antegrade stenting; RBO: Recurrent biliary obstruction; G: Gauge; TRBO: Time to recurrent biliary obstruction.
- Citation: Sugimoto M, Nakajima Y, Takeda Y, Sato Y, Takagi T, Suzuki R, Asama H, Shimizu H, Sato K, Ohira R, Nakamura J, Kato T, Yanagita T, Otsuka M, Hikichi T, Ohira H. Efficacy and safety of plastic and metal stents for endoscopic ultrasound guided-biliary drainage in elderly patients. World J Gastrointest Endosc 2025; 17(12): 110136
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5190/full/v17/i12/110136.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4253/wjge.v17.i12.110136