©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastrointest Endosc. Jan 16, 2025; 17(1): 101119
Published online Jan 16, 2025. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v17.i1.101119
Published online Jan 16, 2025. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v17.i1.101119
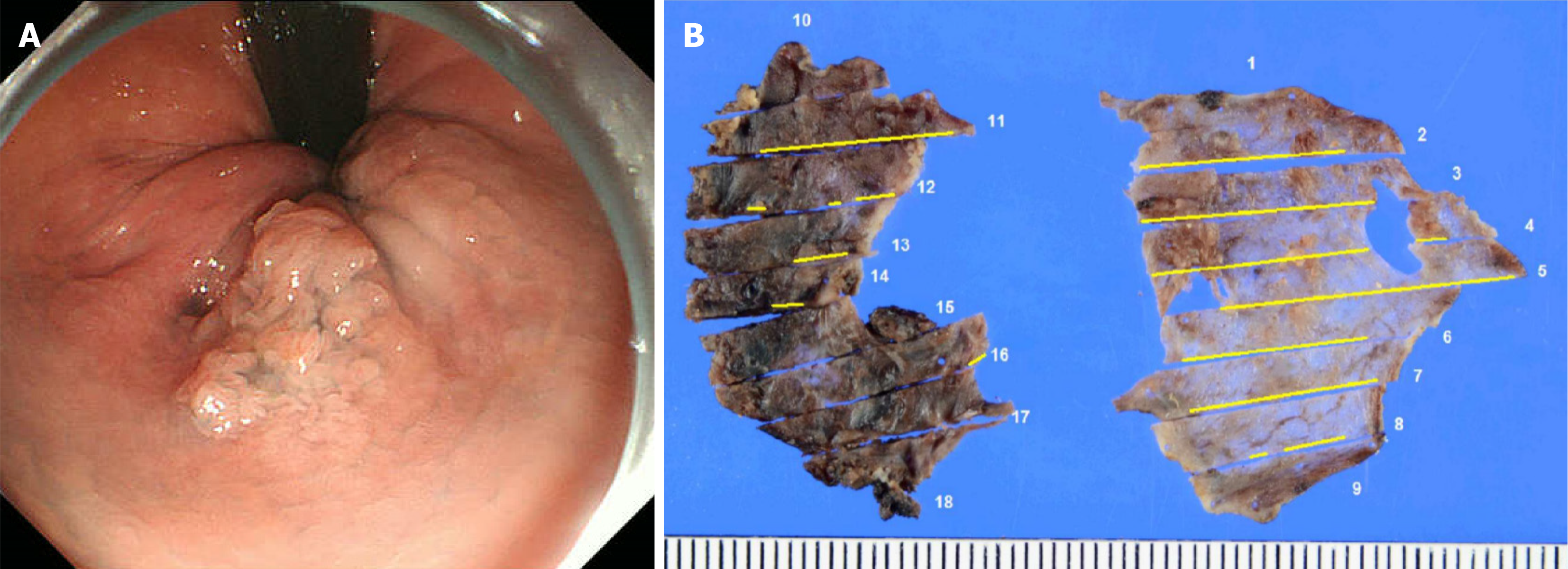
Figure 1 Endoscopic image at initial presentation.
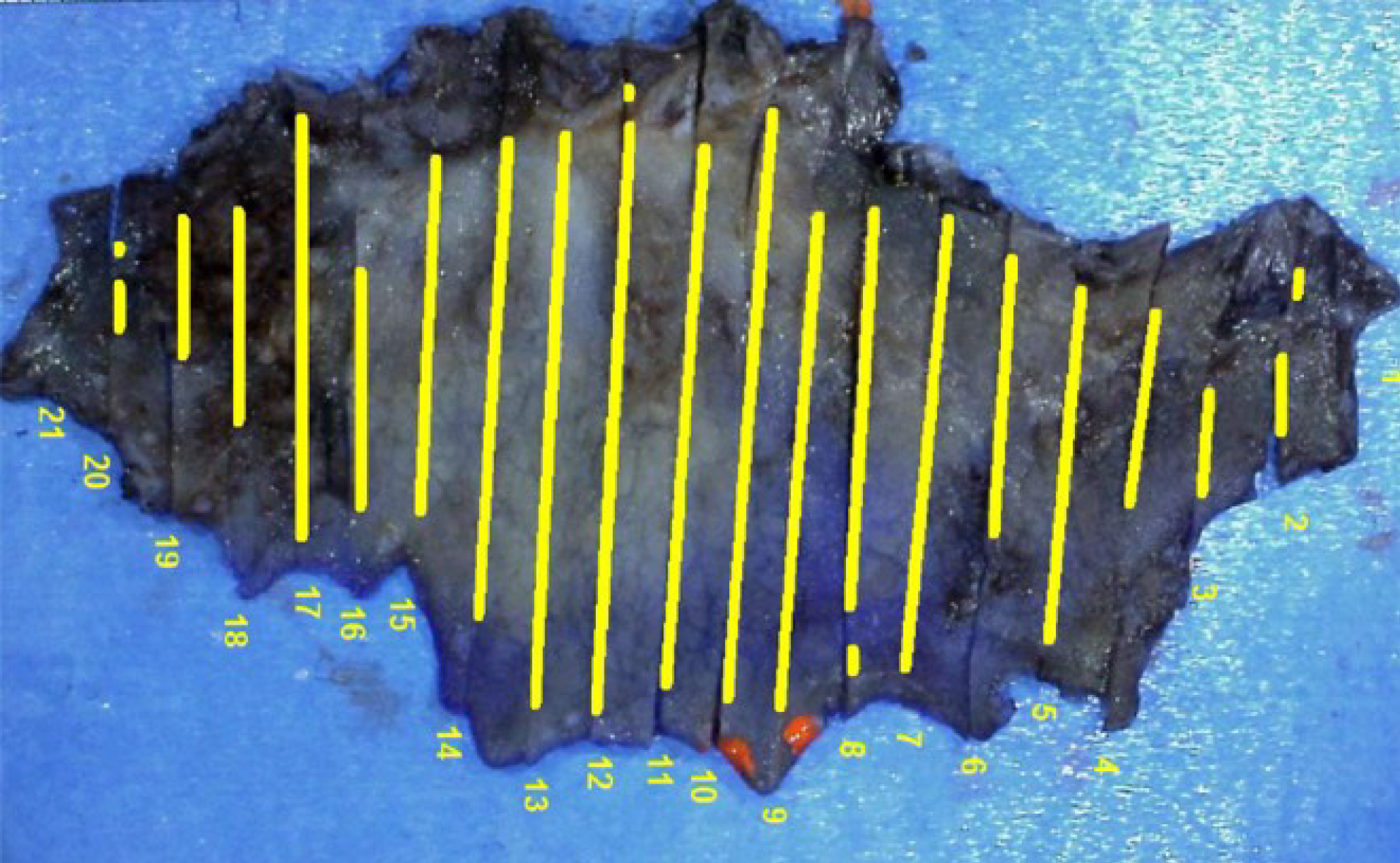
A: A 20-mm elevated lesion on the left wall of the anal canal; B: The number represents the cross section, and the tumor is identified by the yellow line. But the specimen was removed in two sections. Therefore, it was difficult to evaluate.
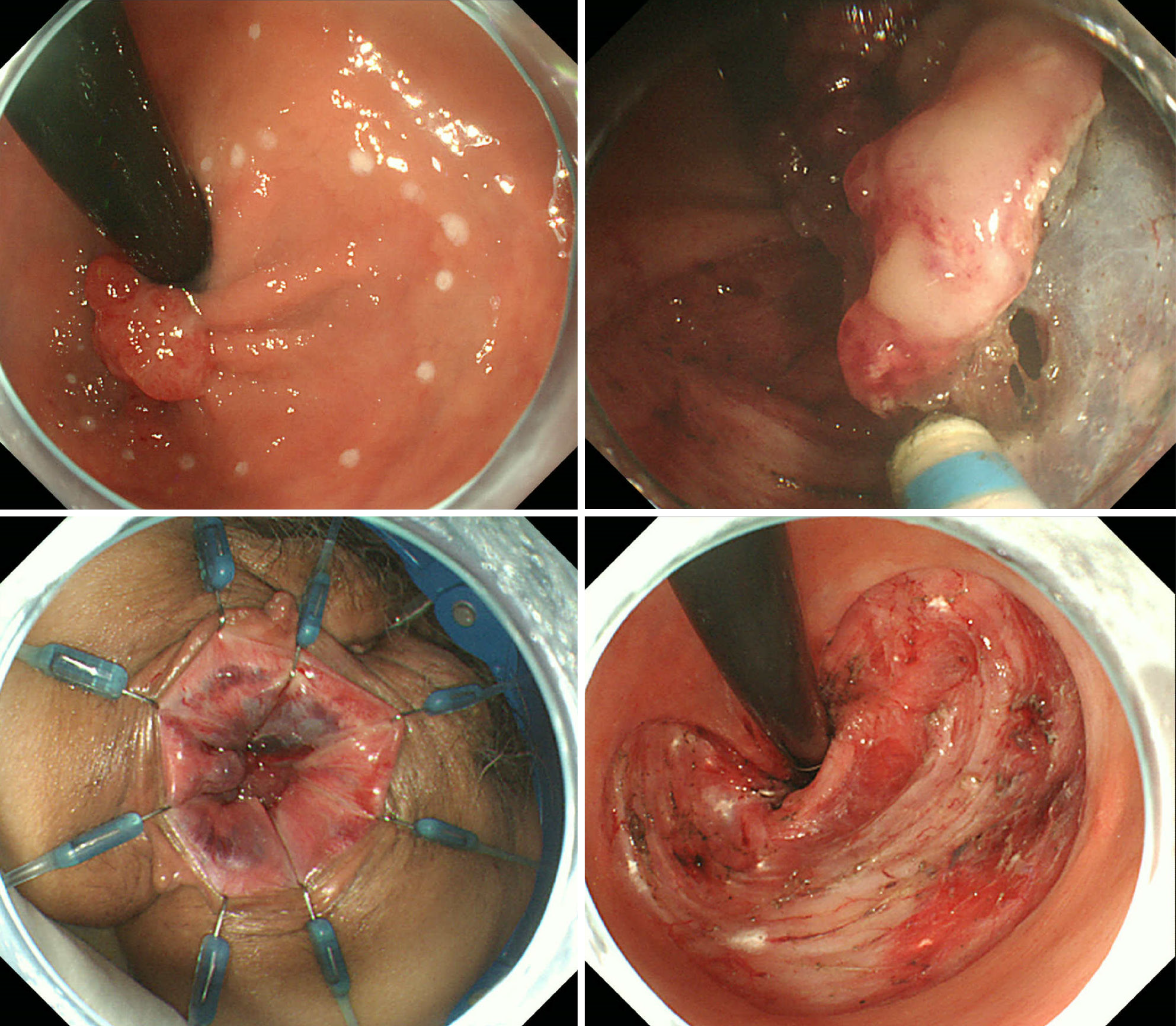
Figure 2 The entire circumference was marked, and endoscopic submucosal dissection and transanal resection were performed.
The specimen was resected without damage.
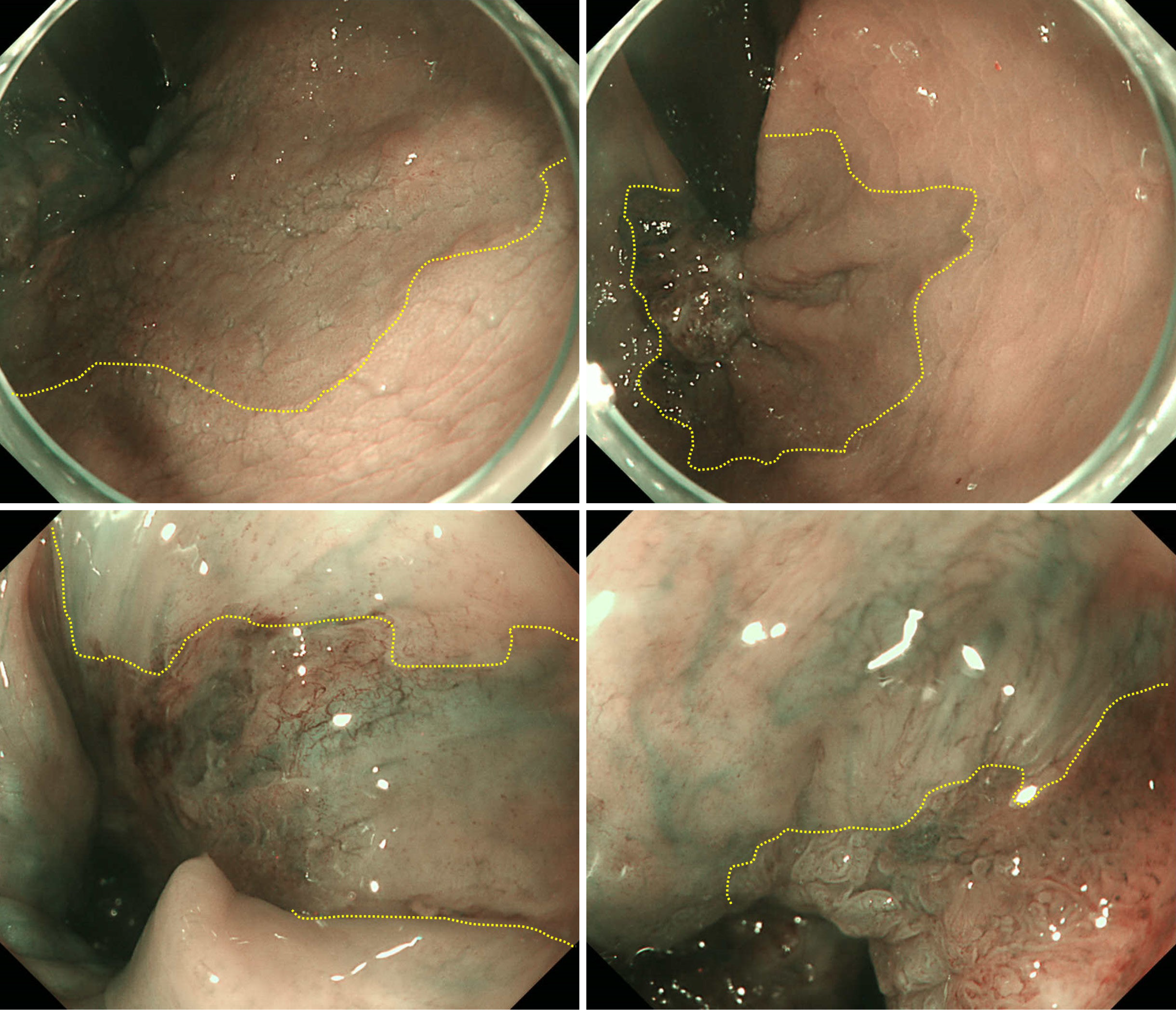
Figure 3 A 20-mm Isp lesion on the left anterior wall of the rectum.
The demarcation line is observed circumferentially using narrow band imaging.
Figure 4 The number represents the cross section, and the tumor is identified by the yellow line.
The specimen was removed without damage.
- Citation: Kinoshita M, Maruyama T, Hike S, Hirosuna T, Kainuma S, Kinoshita K, Nakano A, Ohira G, Uesato M, Matsubara H. Complete resection of recurrent anal canal cancer using endoscopic submucosal dissection and transanal resection: A case report. World J Gastrointest Endosc 2025; 17(1): 101119
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5190/full/v17/i1/101119.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4253/wjge.v17.i1.101119