©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Gastrointest Endosc. Jun 16, 2024; 16(6): 273-281
Published online Jun 16, 2024. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v16.i6.273
Published online Jun 16, 2024. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v16.i6.273
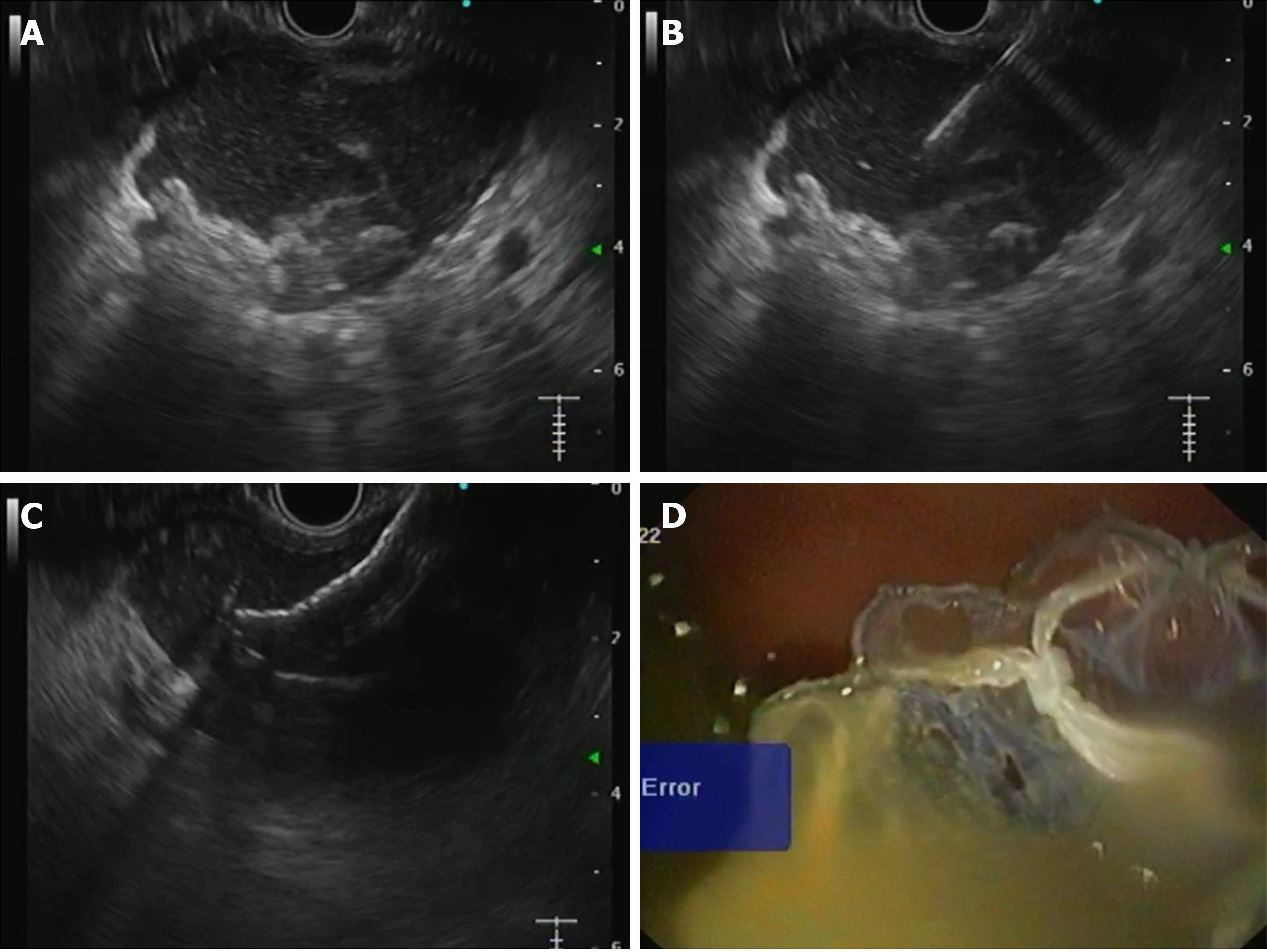
Figure 1 Endoscopy.
A: A walled-off collection with hyperechoic necrotic contents; B: The collection was punctured with a 19-gauge needle; C: Proximal flange of the metal stent was deployed under endoscopic ultrasound vision; D: Distal flange of the stent was deployed under endoscopic vision.
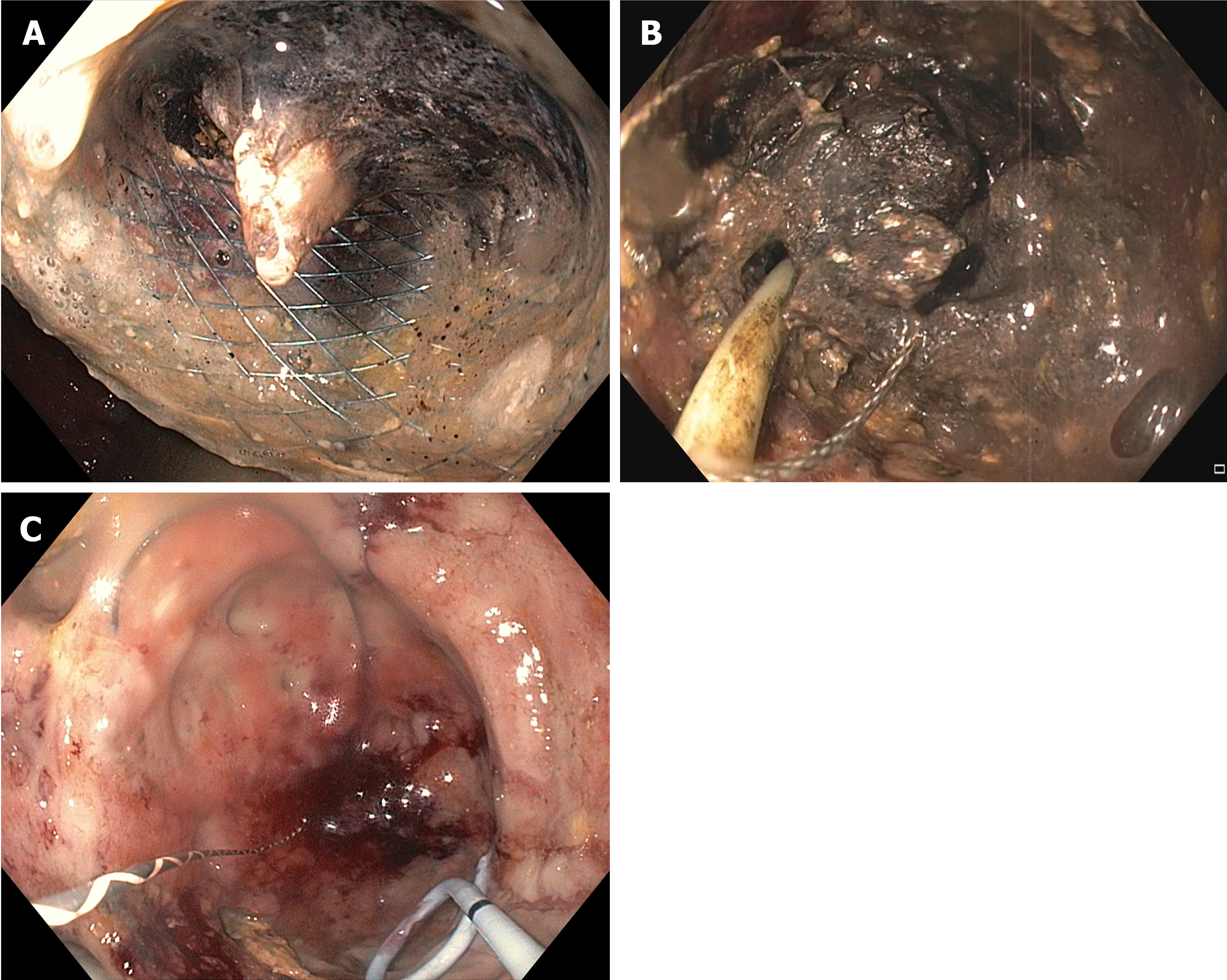
Figure 2 Process of entering the cavity through the cystoenterostomy tract and the removal of solid material.
A: The metal stent was blocked due to the necrotic material; B: Debris was removed with direct endoscopic necrosectomy using a snare; C: A double pigtail plastic stent was placed to replace the metal stent.
- Citation: Singh AK, Manrai M, Kochhar R. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided pancreatic fluid collection drainage: Where are we? World J Gastrointest Endosc 2024; 16(6): 273-281
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5190/full/v16/i6/273.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4253/wjge.v16.i6.273