©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Gastrointest Endosc. May 16, 2020; 12(5): 138-148
Published online May 16, 2020. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v12.i5.138
Published online May 16, 2020. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v12.i5.138
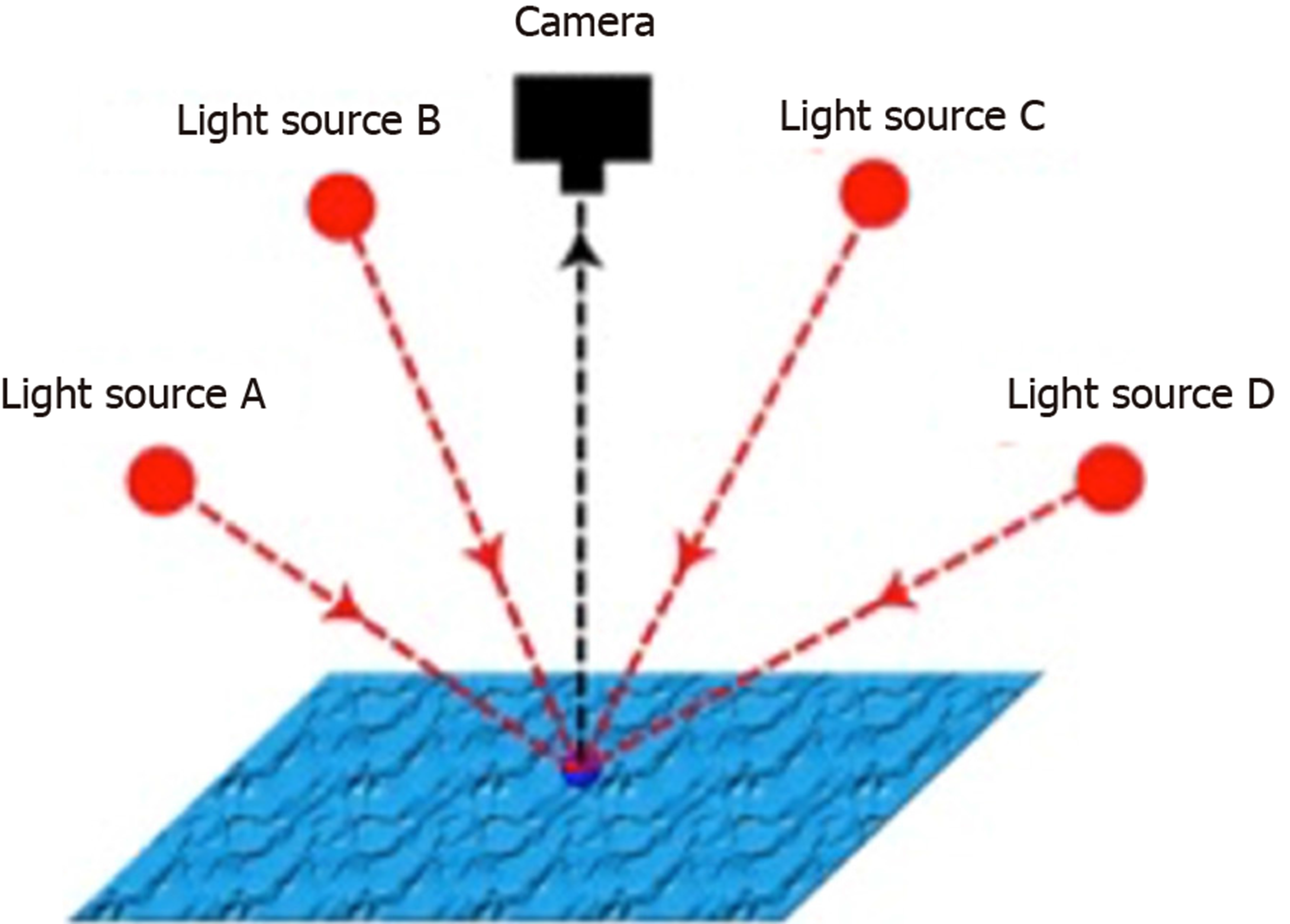
Figure 1 Principles of photometric stereo.
A single fixed viewpoint captures multiple images of a surface illuminated by differently orientated light sources. The known properties of the viewpoint and light sources can be used to derive the surface orientation, which is not known, from the image series. (Courtesy of Smith ML, co-author).
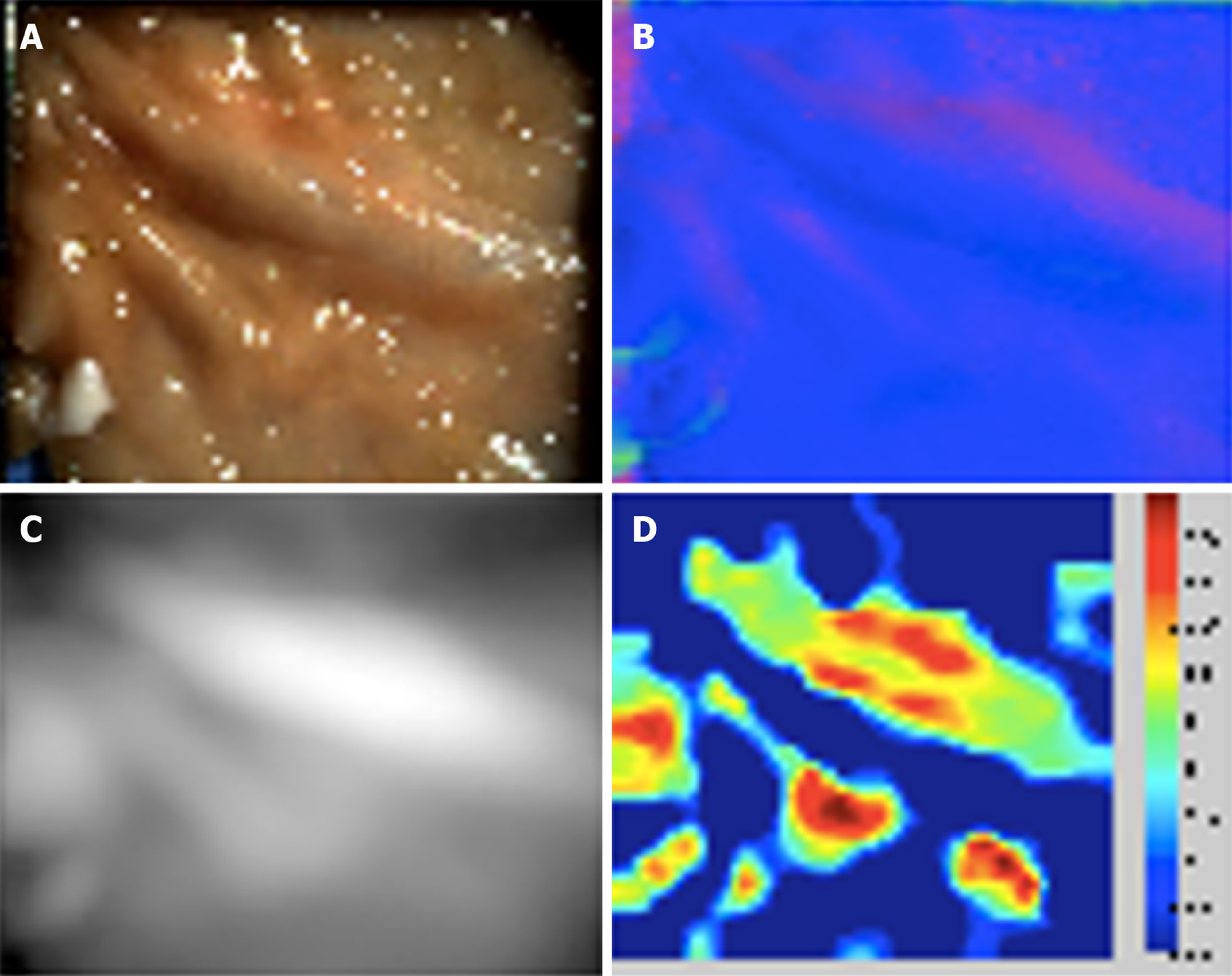
Figure 2 Porcine colonic mucosa captured with photometric stereo imaging.
A: One of six captured white light images; B: Reconstructed surface normal map; C: Reconstructed height map; D: Shape Index plot. (Courtesy of Poullis A, co-author).
Figure 3 Phantom polyp differentiation using the Shape Index.
A spherical phantom polyp is differentiated from adjacent normal tissue by applying a hysteresis thresholding technique to the Shape Index. (Courtesy of Poullis A, co-author).
- Citation: Shandro BM, Emrith K, Slabaugh G, Poullis A, Smith ML. Optical imaging technology in colonoscopy: Is there a role for photometric stereo? World J Gastrointest Endosc 2020; 12(5): 138-148
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5190/full/v12/i5/138.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4253/wjge.v12.i5.138