©The Author(s) 2018.
World J Gastrointest Endosc. Sep 16, 2018; 10(9): 156-164
Published online Sep 16, 2018. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v10.i9.156
Published online Sep 16, 2018. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v10.i9.156
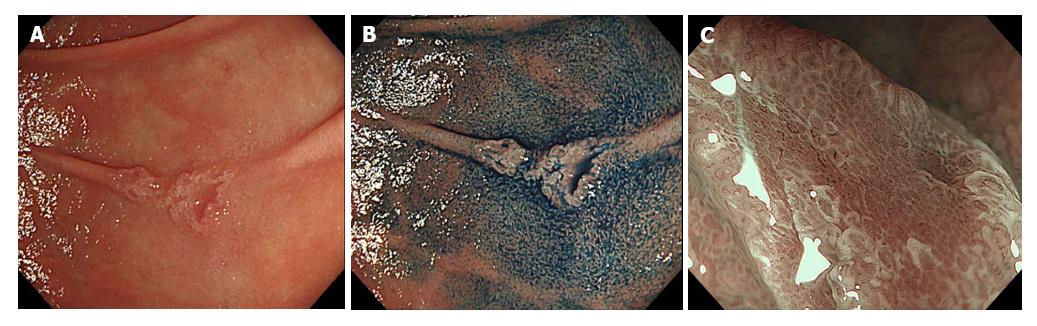
Figure 1 Endoscopic findings of a superficial non-ampullary duodenal tumor.
A: A shallow depressed lesion (IIc) is observed in the second portion of the duodenum; B: Chromoendoscopy with indigo carmine; C: Magnifying endoscopy with narrow band imaging.
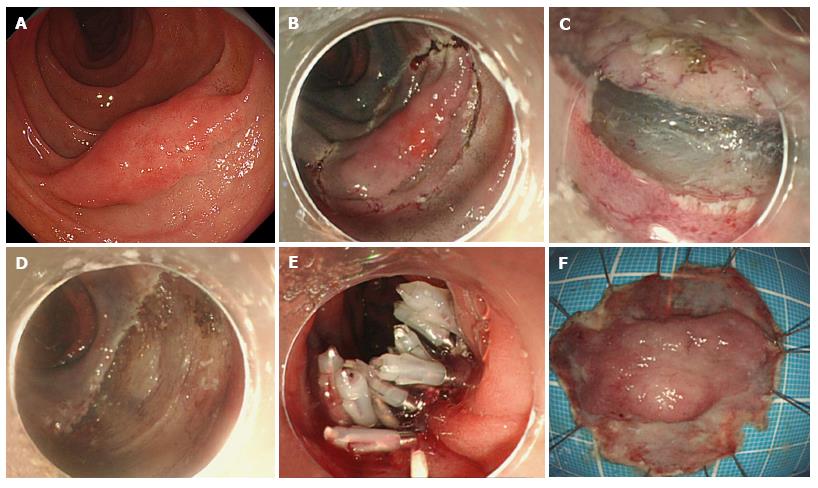
Figure 2 Endoscopic submucosal dissections for a superficial non-ampullary duodenal tumor.
A: Protruded sessile type (Is) larger ≥ 20 mm in size; B: Mucosal incision around the lesion; C: Submucosal dissection of the lesion after mucosal incision; D: Mucosal defect after endoscopic submucosal dissection; E: Closure of mucosal defect using multiple endoclips; F: Resected specimen.
- Citation: Esaki M, Suzuki S, Ikehara H, Kusano C, Gotoda T. Endoscopic diagnosis and treatment of superficial non-ampullary duodenal tumors. World J Gastrointest Endosc 2018; 10(9): 156-164
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5190/full/v10/i9/156.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4253/wjge.v10.i9.156