Copyright
©The Author(s) 2006.
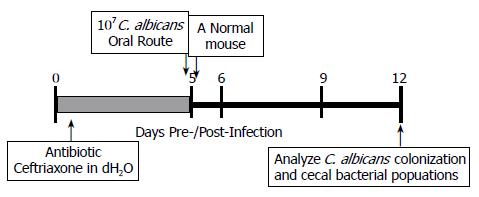
图1 构建抗生素治疗诱导的胃肠道C.
albicans定植小鼠模型.
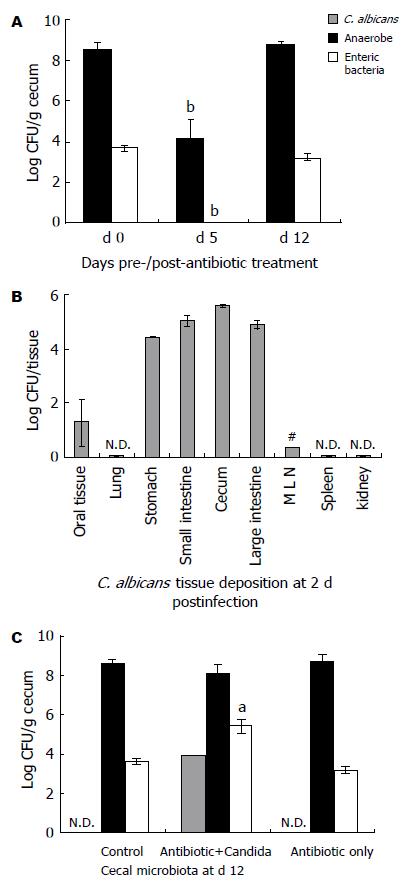
图2 抗生素处理对胃肠道微生物区系的影响.
A: Cecal bacterial populations before and after antibiotic treatment, bP<0.01; B: C. albicans tissue deposition at 2 d postinfection, MLN, mesenteric lymph node. #, 2/8 mice lead to C. albicans translocation at 48 h postinfection; C: Cecal microbiota populations at 7 d postinoculation with C. albicans. n = 7 to 8 mice per time point pooled from two separate experiments, aP<0.05. ND, not detected (<50 CFU).
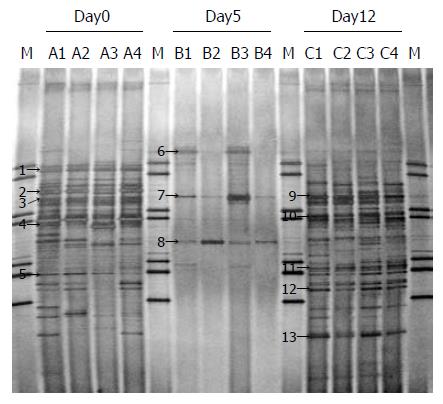
图3 抗生素处理前后盲肠细菌微生物区系16S rDNA V3引物的DGGE图谱.
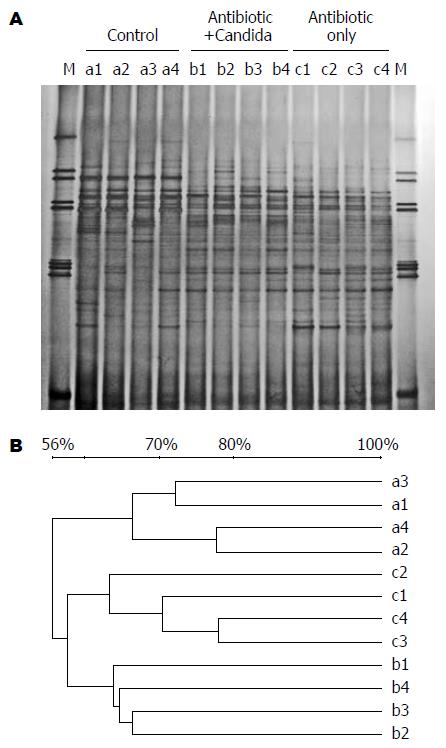
图4 盲肠细菌微生物区系16S rDNA V3引物的DGGE图谱(A)和UPGMA相似性聚类分析(B).
引文著录: 黄雪峰, 袁静, 魏泓. 抗生素诱导SPF级BALB/c小鼠胃肠道白念珠菌定植模型. 世界华人消化杂志 2006; 14(12): 1161-1166